STAR Offline QA Shift Histogram Description - Run 6
Note:
Not all reference plots may be ideal, be sure to carefully read the
descriptions.
This page contains the reference histograms and descriptions for the
Offline QA system for Run 6. These pages should correspond
exactly to the jobs viewed in the Offline QA Browser. However,
STAR is a dynamic experiment and the plots generated for QA will change
several times throughout the run. If this reference page seems
out-of-date, or if you find a job that would make a better reference,
please email the QA hypernews list here.
Other links:
Michael Daugherity for the QA Team.
April 2, 2006.
Page Index for QA Shift Plots
Page 1
Page 2
Page 3
Page 4
Page 5
Page 6
Page 7
Page 8
Page 9
Page 10
Page 11
Page 12
Page 13
Page 14
Page 15
Page 16
Page 17
Page 18
Page 19
Page 1
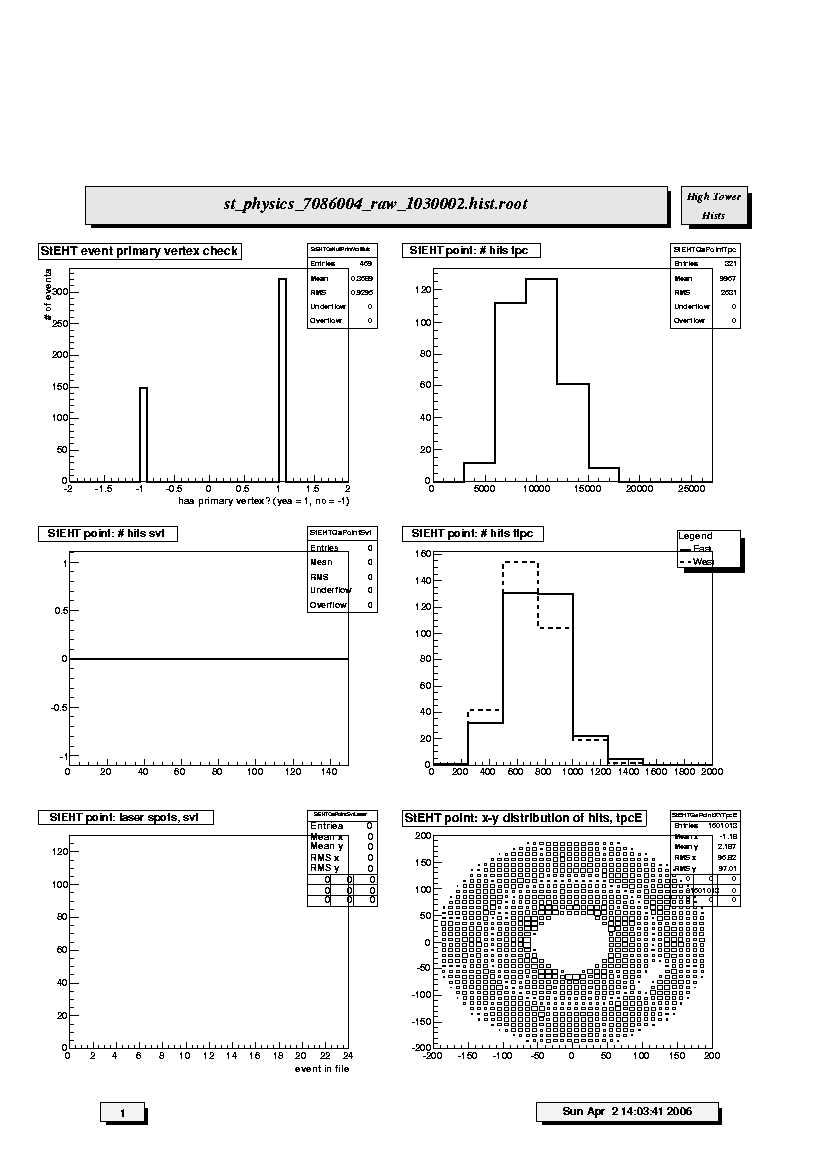
1. StEHT event primary vertex check:
Primary vertex finding status for run; events with (1) and without (-1)
final vertex. The relative fraction of events with primary vertex
depends on trigger, beam diamond width and position.
2. StEHT point: # hits tpc:
Distribution of number of reconstructed space points in TPC per
event. Should scale with centrality, depends on multiplicity cut for
this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
3. StEHT point: # hits svt:
Distribution of number of reconstructed space points in SVT per event.
Should scale with centrality, depends on multiplicity cut for this set
of plots (i.e. low, medium or high). Also depends strongly on vertex
position distribution.
4. StEHT point: # hits ftpc:
Distribution of number of reconstructed space points in FTPC East (solid
line) and West (dashed line) per event. Should have similar means and
widths; scales with centrality, depends on multiplicity cut for this set
of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
5. StEHT point: laser spots, svt:
Stability of laser spot positions in time bin (vertical axis) as
function of event number. The position of the laser spots should be
constant over time (event number), meaning that the SVT is in thermal
equilibrium. Three laser positions are shown.
6. StEHT point: x-y distribution of hits, tpcE:
Scatter plot of the azimuthal distribution of reconstructed space points
in the East TPC. The distribution should be azimuthally uniform exept
for the 12 sector structure of the TPC (lighter areas indicate sector
boundaries). Density should decrease radially but inner and outer sector
structure should be present (darker areas in the innermost pads of the
inner and outer sectors). Watch for empty areas (typically masked RDOs)
and hot spots. Notify if new empty area or hot spot appears.
Page 2
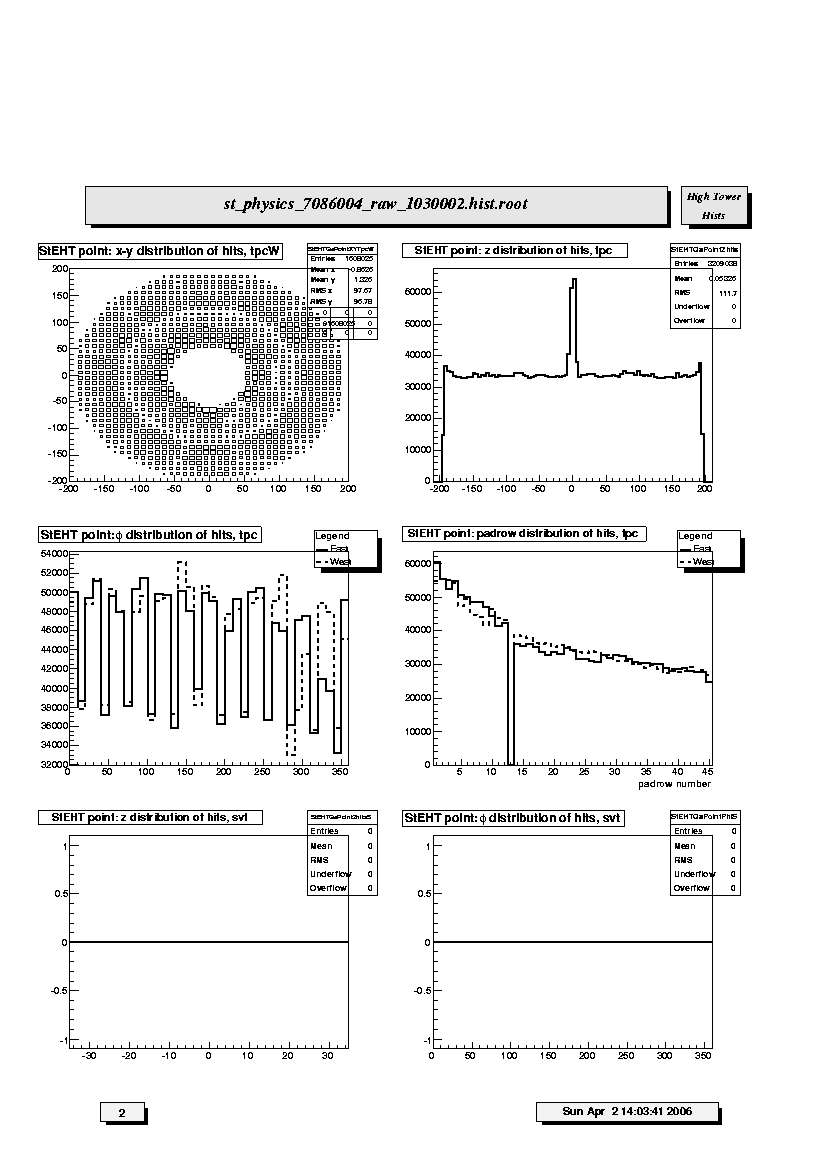
1. StEHT point: x-y distribution of hits, tpcW:
Scatter plot of the azimuthal distribution of reconstructed space points
in the West TPC. The distribution should be azimuthally uniform exept
for the 12 sector structure of the TPC (lighter areas indicate sector
boundaries). Density should decrease radially but inner and outer sector
structure should be present (darker areas in the innermost pads of the
innear and outer sectors). Watch for empty areas (typically masked RDOs)
and hot spots. Notify if new empty area or hot spot appears.
2. StEHT point: z distribution of hits, tpc:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in TPC with respect to
z-coordinate. Should be flat within statistics. Watch out for anamolous
peaks at z=0 (central membrane), steps or unusual spikes or dips. Some
roll-off at the ends is normal.
3. StEHT point: phi distribution of hits, tpc:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in TPC with respect to
azimuthal coordinate (phi) for east (solid line) and west (dashed line)
halves. Should be flat except for the 12-fold sector structure or masked
RDOs (as shown). Dead RDO's will produce dips and gaps; hot pads or
FEE cards will produce spikes.
4. StEHT point: padrow distribution of hits, tpc:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in TPC with respect to padrow
number 1-45. Should display gradual fall-off; watch for anamolous spikes
and dips. Padrow 13 has been masked out and thus must be empty.
5. StEHT point: z distribution of hits, svt:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in SVT with respect to
z-coordinate. Should be flat within statistics with step like drop off
at larger abs(z) due to SVT barrel structure. Depends on distribution of
collision vertices.
6. StEHT point: phi distribution of hits, svt:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in SVT with respect to
azimuthal coordinate (phi). Should be flat within statistics.
Page 3
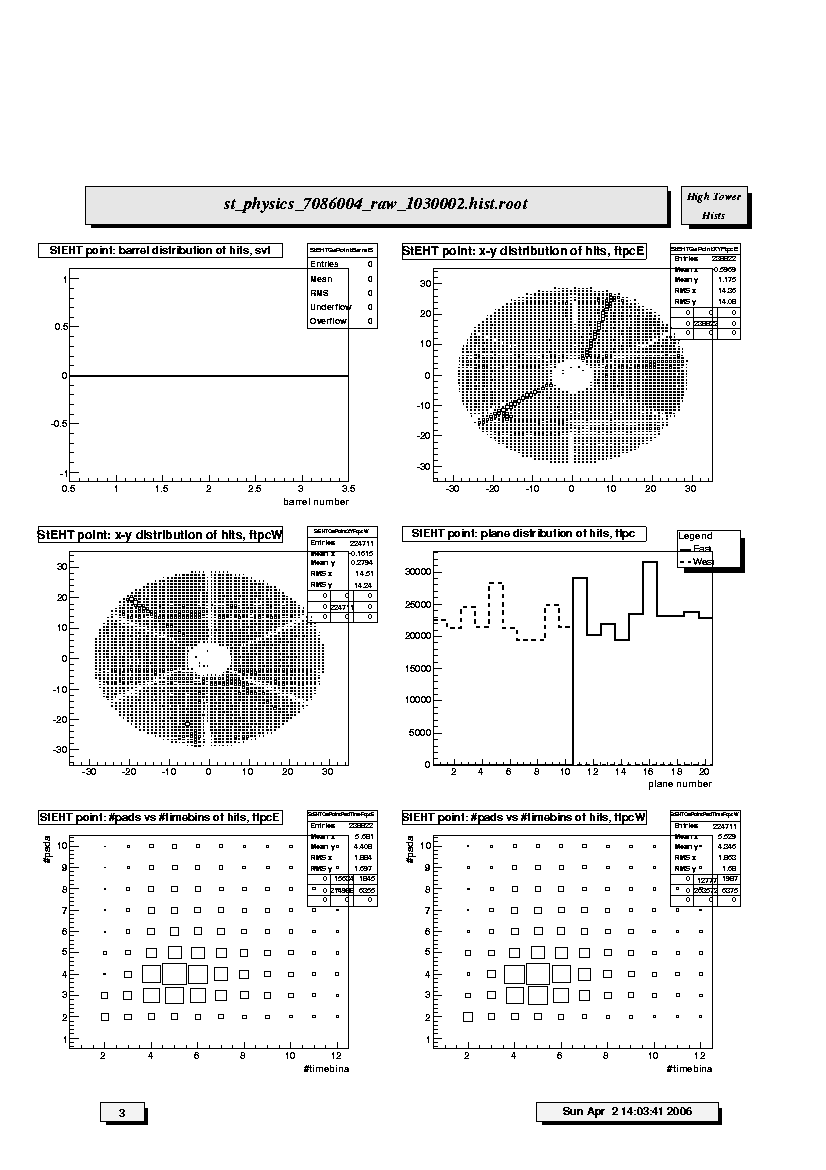
1. StEHT point: barrel distribution of hits, svt:
Distribution of reconstructed space points in SVT with respect to barrel
number 1-3. Should have larger number in outer 2 barrels than the first.
2. StEHT point: x-y distribution of hits, ftpcE:
Radial distribution of reconstructed space points in FTPC East. The distribution should be uniform
except for the insensitive gaps between the readout sectors. Localized denser areas are due to noise.
Ideally noisy pads are flagged in the FTPC gain tables so that they are not used for cluster finding.
Less densely populated areas not on the sector boundaries are due to dead electronics. Empty areas
not on the sector boundaries indicates a serious hardware problem. An FTPC expert should be contacted
immediately if this is seen in fast offline-QA during data taking.
3. StEHT point: x-y distribution of hits, ftpcW:
Radial distribution of reconstructed space points in FTPC West. The distribution should be uniform
except for the insensitive gaps between the readout sectors. Localized denser areas are due to noise.
Ideally noisy pads are flagged in the FTPC gain tables so that they are not used for cluster finding.
Less densely populated areas not on the sector boundaries are due to dead electronics. Empty areas
not on the sector boundaries indicates a serious hardware problem. An FTPC expert should be contacted
immediately if this is seen in fast offline-QA during data taking.
4. StEHT point: plane distribution of hits, ftpc:
Number of reconstructed space points assigned to tracks in FTPC East (solid line) and
West (dashed line) in each padrow. The horizontal axis shows padrow numbers where FTPC-West
is 1-10 and FTPC-East is 11-20. Padrows #1 and #11 are closest to the center of STAR. East
and West should be similar in shape and magnitude. Spikes indicate noisy electronics; dips indicate dead electronics.
5. StEHT point: #pads vs #timebins of hits, ftpcE
Monitors the cluster quality in FTPC East. Ideally the clusters should have a pad length of 3-5
and a timebin length of 4-6. A prominent peak located at (2,2) indicates bad gas or loss of gain or excessive background.
6. StEHT point: #pads vs #timebins of hits, ftpcW
Monitors the cluster quality in FTPC West. Ideally the clusters should have a pad length
of 3-5 and a timebin length of 4-6. A prominent peak located at (2,2) indicates bad gas or loss of gain or excessive background.
Page 4
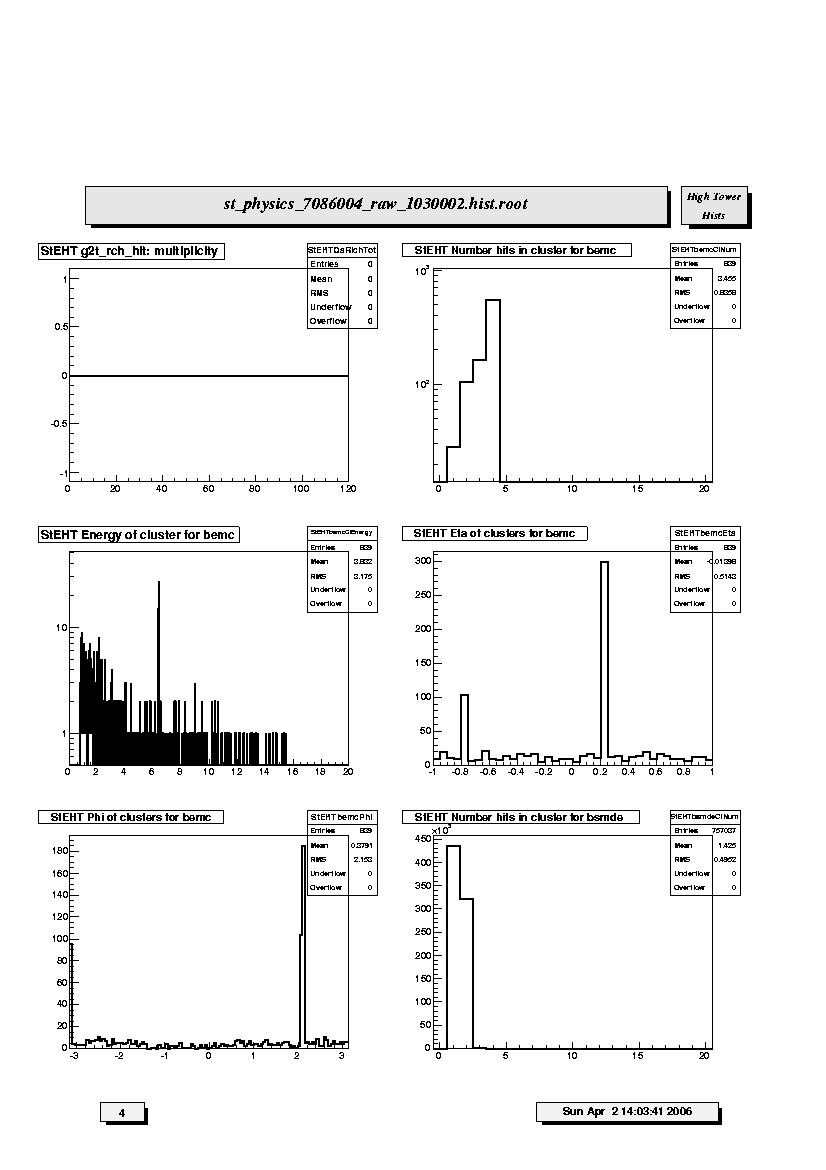
1. StEHT g2t_rch_hit: multiplicity:
Hit distribution in RICH detector (now obsolete - ignore).
2. StEHT Number hits in cluster for bemc:
Distribution of number of BEMC towers contributing to energy clusters.
3. StEHT Energy of cluster for bemc:
Distribution of energy in reconstructed clusters in EMC barrel.
4. StEHT Eta of clusters for bemc:
Integrated pseudorapidity distribution of reconstructed energy clusters
in the EMC-barrel. Note there will be gaps due to missing and/or
uninstrumented sectors. Report any unexpected gaps or unusual spikes.
In 2005 (as of January) only the eta > 0 half is instrumented.
5. StEHT Phi of clusters for bemc:
Integrated azimuthal distribution (radians) of reconstructed energy
clusters in the EMC-barrel. Note there will be gaps due to missing
and/or uninstrumented sectors. Report any unexpected gaps or unusual
spikes.
6. StEHT Number hits in cluster for bsmde:
Distribution of numbers of hits (anodes) contributing to Barrel SMD
clusters along pseudorapidity.
Page 5
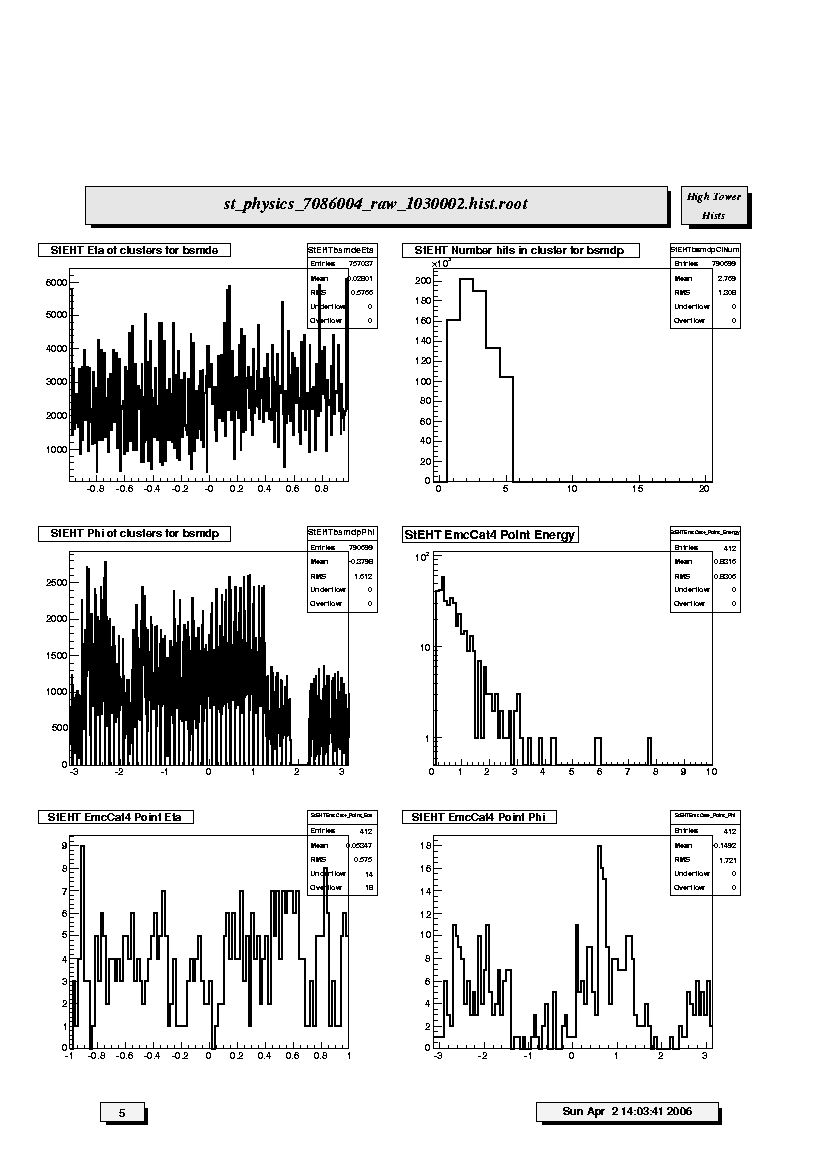
1. StEHT Eta of clusters for bsmde:
Pseudorapidity distribution of reconstructed energy clusters in the BSMD
anode grid along pseudorapidity. Note there will be gaps due to
missing and/or uninstrumented sectors. Report any unexpected gaps or
unusual spikes.
2. StEHT Number hits in cluster for bsmdp:
Distribution of numbers of hits (anodes) contributing to Barrel SMD
clusters along azimuth.
3. StEHT Phi of clusters for bsmde:
Azimuthal (radian) distribution of reconstructed energy clusters in the
BSMD anode grid along azimuthal (phi). Note there will be gaps due to
missing and/or uninstrumented sectors. Report any unexpected gaps or
unusual spikes.
4. StEHT EmcCat4 Point Energy:
Energy distribution for Barrel EMC-SMD Category 4 clusters. Cat4
clusters correspond to TPC track matched clusters in the EMC barrel,
BSMD-eta and BSMD-phi detectors.
5. StEHT EmcCat4 Point Eta:
Pseudorapidity distribution for EMC-SMD Category 4 clusters.
6. StEHT EmcCat4 Point Phi:
Azimuthal distribution for EMC-SMD Category 4 clusters.
Page 6
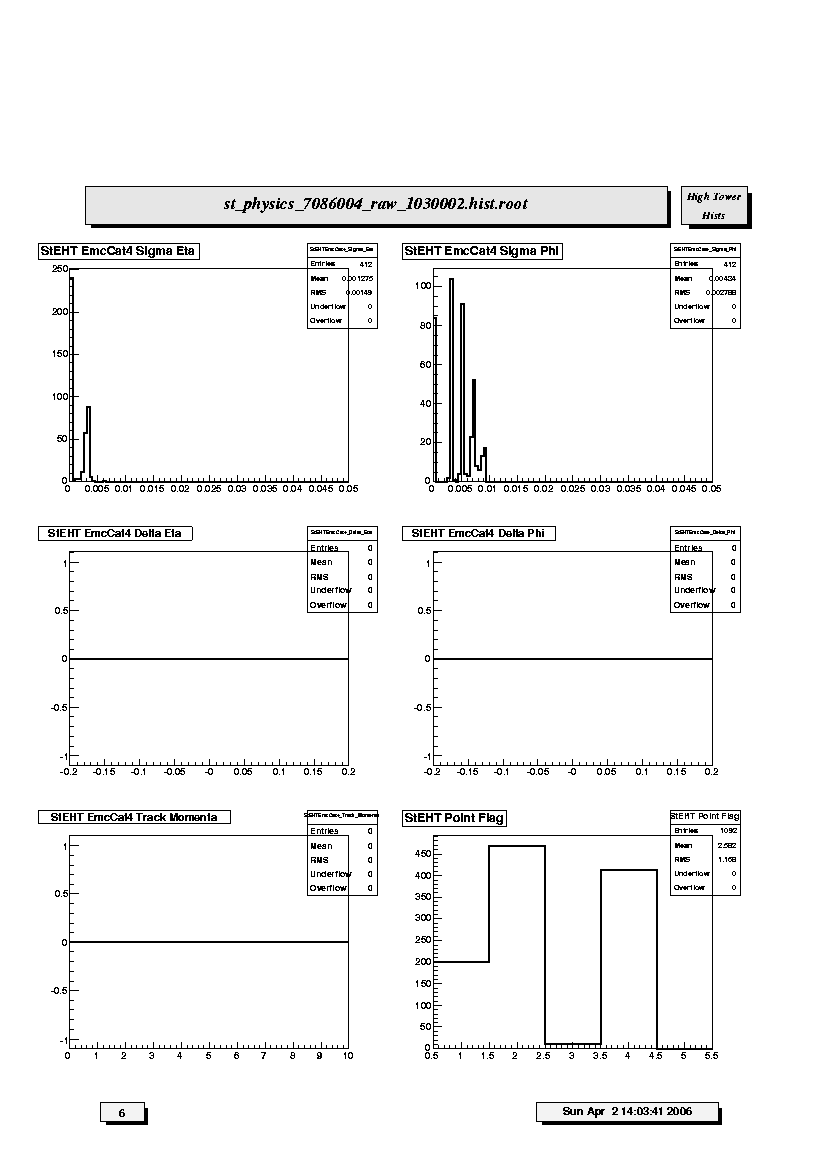
1. StEHT EmcCat4 Sigma Eta:
Distribution of widths (sigma) of Category 4 Barrel EMC-SMD clusters
with respect to pseudorapidity.
2. StEHT EmcCat4 Sigma Phi:
Distribution of widths (sigma) of Category 4 Barrel EMC-SMD clusters
with respect to azimuthal angle.
3. StEHT EmcCat4 Delta Eta:
Differences between centroids of Category 4 Barrel EMC-SMD clusters and
projected positions of TPC tracks at BEMC with respect to
pseudorapidity. Should be peaked at ~0.
4. StEHT EmcCat4 Delta Phi:
Differences between centroids of Category 4 Barrel EMC-SMD clusters and
projected positions of TPC tracks at BEMC with respect to azimuthal
angle. Should be peaked at ~0.
5. StEHT EmcCat4 Track Momenta:
Distribution of TPC global track momentum for Barrel EMC-SMD Category 4
clusters.
6. StEHT Point Flag:
Distribution of Barrel EMC and SMD cluster types by Category number.
There should be a reasonable fraction of Cat4 clusters; report if
less than 10% of total.
Page 7
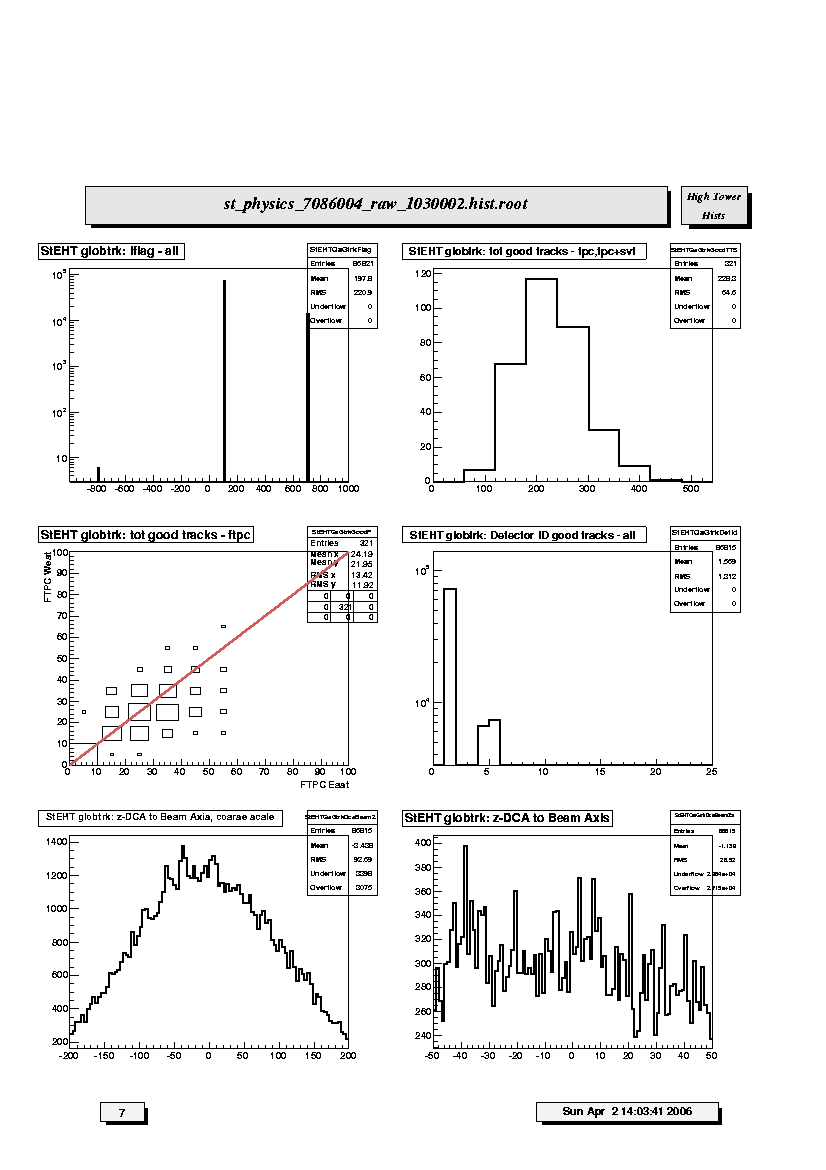
1. StEHT globtrk:iflag - all:
Quality flag values for all global tracks. Some with large, negative
values may not appear on plot; check stat. box for underflows. Majority
of tracks should have iflag>0, corresponding to good, usable tracks.
Refer to: dst_track_flags.html and kalerr.html for description of flag
values.
2. StEHT globtrk: tot good tracks - tpc, tpc+svt:
Global track multiplicity distribution for TPC-only and SVT+TPC tracks.
Magnitude and width depends on trigger condition and multiplicity cut
for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
3. StEHT globtrk: tot good tracks - ftpc:
Scatter plot of good global track multiplicities in FTPC West versus
FTPC East. Distribution should be correlated and lie along the reference
diagonal line, depending on the relative fraction of active readout in
the East and West detectors. Magnitudes and widths depend on trigger
condition and multiplicity cut for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium
or high).
4. StEHT globtrk: Detector ID good tracks - all:
Global track detector IDs for good tracks. Refer to:
/afs/rhic/star/packages/DEV00/pams/global/inc/StDetectorDefinitions.h
for Detector ID codes.
5. StEHT globtrk: z-DCA to Beam Axis, coarse scale:
Coarse scale distribution along the z-axis (from -200 to +200 cm) of the
DCA points to the nominal beam line (z-axis, x=y=0) for all TPC and
SVT+TPC global tracks. Peaks indicate probable locations of individual
collision vertices. There should be many peaks corresponding to the RHIC
beam-beam collision region. Indentification of individual p-p collision
vertices is unlikely.
6. StEHT globtrk: z-DCA to Beam Axis:
Fine scale distribution along the z-axis (from -50 to +50 cm) of the DCA
points to the nominal beam line (z-axis, x=y=0) for all TPC and SVT+TPC
global tracks. Peaks indicate probable locations of individual collision
vertices. Peaks near the center should be narrower than those beyond
about 25 cm due to variations in the effective radiation thickness of
the SVT assembly along the z-axis. Indentification of individual p-p collision
vertices is unlikely.
Page 8
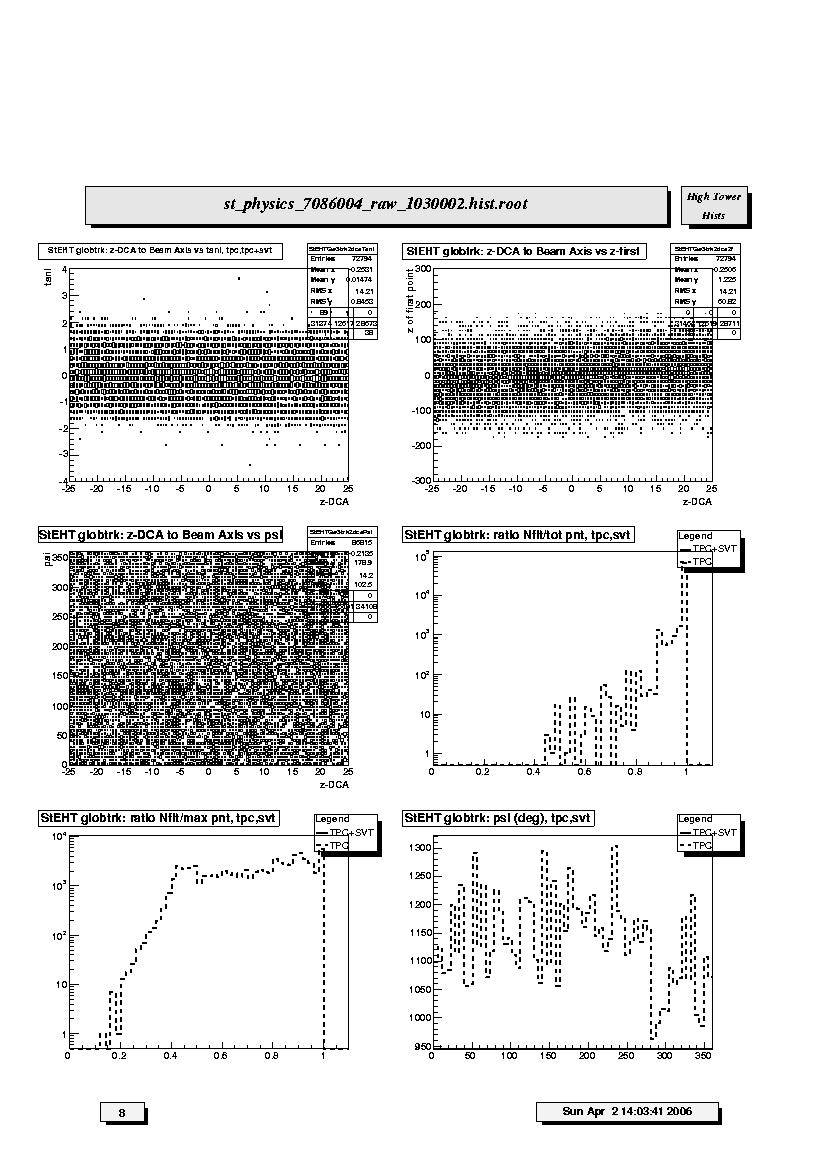
1. StEHT globtrk: z-DCA to Beam Axis vs tan1,tpc,tpc+svt:
Scatter plot of the tangent of the dip angle (tanl) versus the
z-coordinate (from -25 to 25 cm) of the DCA points to the nominal beam
line (z-axis, x=y=0) for all TPC and SVT+TPC global tracks. Vertical
bands should be seen corresponding to individual events. The bands
should be smooth and continuous; breaks at tanl=0 indicate probable TPC
calibration errors in either the t0 offset or the drift speed.
This is best seen for high multiplicity events.
Cross reference for calibration errors with z of first hit (9.6).
Indentification of individual p-p collision bands is unlikely.
2. StEHT globtrk: z-DCA to Beam Axis vs z-first
Scatter plot of the z-coordinate of the first fitted hit in the TPC
versus the z-coordinate (from -25 to 25 cm) of the DCA points to the
nominal beam line (z-axis, x=y=0) for all TPC-only global tracks and
SVT+TPC global tracks in which the first point used in the fit lies in
the TPC (i.e. SVT assigned hits are thrown out during the fitting
process). Vertical bands should be seen corresponding to individual
events. The bands should be smooth and continuous; breaks at z=0
indicate TPC calibration errors in either the t0 offset or the drift
speed. This is best seen for high multiplicity events. This plot is of
limited value compared to the previous due to the SVT which catches most
of the first hits. Indentification of individual p-p collision bands is unlikely.
3. StEHT globtrk: z-DCA to Beam Axis vs psi:
Scatter plot of the azimuthal direction angle (psi) versus the
z-coordinate (from -25 to 25 cm) of the DCA points to the nominal beam
line (z-axis, x=y=0) for all TPC and SVT+TPC global tracks. Vertical
bands should be seen corresponding to individual events. The bands
should be smooth, straight and continuous indicating azimuthal symmetry
in the tracking. Bends or offsets could indicate problems in individual
TPC sectors such as voltage sags or drifts. These are best studied with
high multiplicity events. Indentification of individual p-p collision bands is unlikely.
4. StEHT globtrk: ratio Nfit/tot pnt, tpc, svt:
Ratio of number of fitted points to total points on track for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. Should peak at ~1.
5. StEHT globtrk: ratio Nfit/max pnt, tpc, svt:
Ratio of number of fitted points to estimated maximum number for
TPC-only (dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. Peak at
low value indicates track splitting. Ratio for SVT+TPC global tracks
should peak near 1. Both distributions can extend above 1.
6. StEHT globtrk: psi(deg),tpc,svt:
Azimuthal distributions for track direction angle (psi) for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. Should be flat
within statistics, except for the 12-sector structure in the TPC-only
global tracks.
Page 9
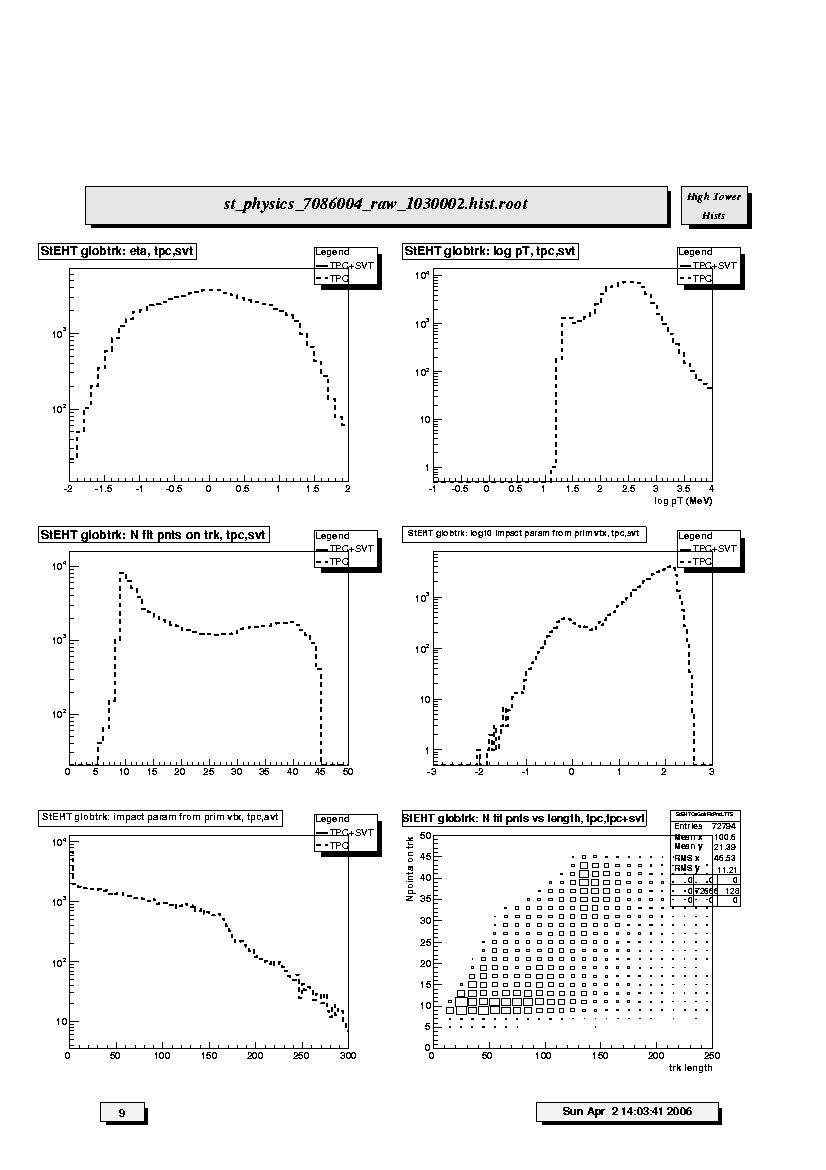
1. StEHT globtrk: eta,tpc,svt:
Pseudorapidity (eta) distributions for TPC-only (dashed line) and
SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. TPC track distribution should be
symmetric about eta=0. SVT+TPC track distribution may be non-symmetric
depending on the distribution of primary vertices.
2. StEHT globtrk: log pT,tpc,svt:
Log-base-10 transverse momentum (GeV/c) distributions for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks.
3. StEHT globtrk: N fit pnts on trk,tpc,svt:
Distribution of the number of fitted points on track for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. Peak at low value
indicates track splitting. Should see an increase near ~40.
4. StEHT globtrk: log 10 impact param from prim vtx,tpc,svgt:
Log-base-10 plot of impact parameter (in cm) from primary vertex for
TPC-only (dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. SVT+TPC
tracks should have much smaller impact parameter values.
5. StEHT globtrk: impact param from prim vtx,tpc,svt:
Linear plot of impact parameter (in cm) from primary vertex for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) global tracks. SVT+TPC tracks
should have much smaller impact parameter values.
6. StEHT globtrk: N fit pnts vs length,tpc,tpc+svt
Scatter plot of number of fitted points on track versus track length
(from first to last point along helical path) for both TPC-only and
SVT+TPC global tracks. Peak in lower left corner indicates split tracks.
There should be some increase for >30 points and lengths from 1 - 2 m.
Page 10
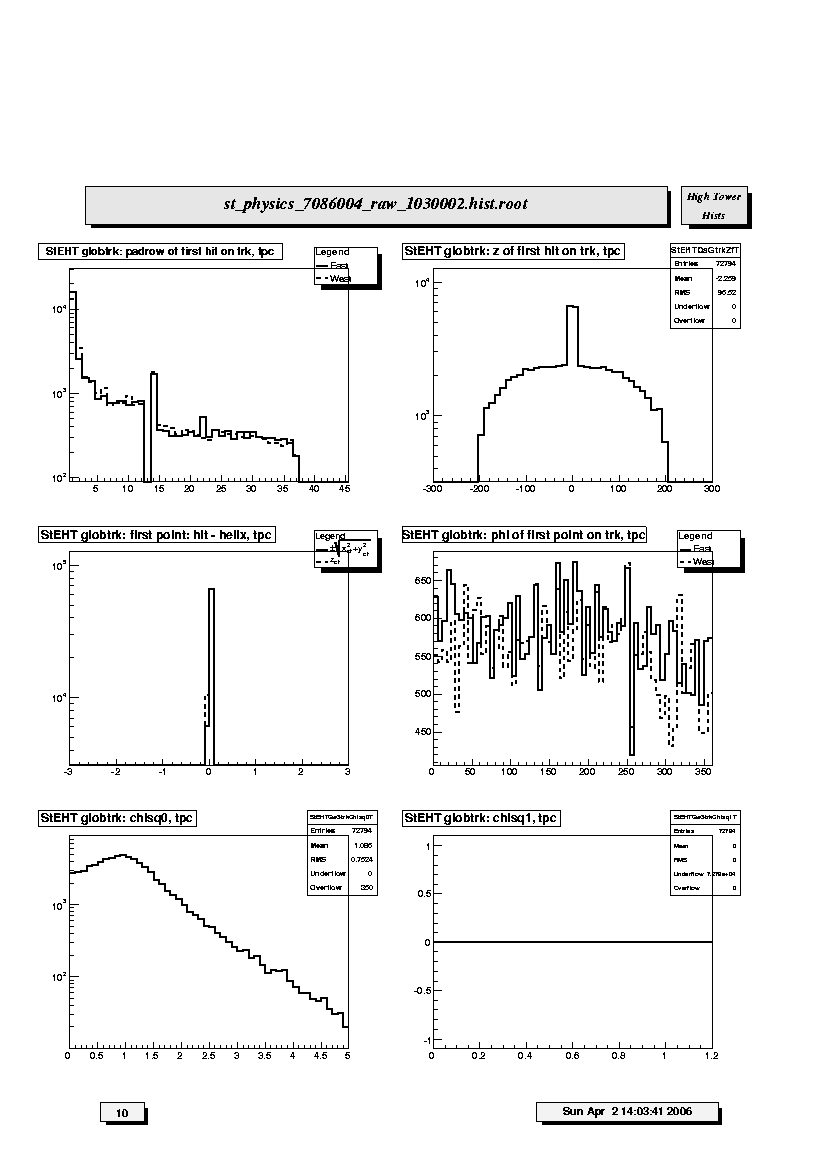
1. StEHT globtrk: padrow of first hit on trk,tpc,svt:
Distribution of first fitted space point with respect to pad row number
for TPC-only global tracks. Should peak at 1 with a minor peak at padrow
14 (beginning of outer sector); the latter should not be too big
relative to that at row 1. Other peaks may indicate large, missing
sections of the TPC read-out causing breaks, and consequently
additional, false new starting points for tracks. Padrow 13 is masked out.
2. StEHT globtrk: z of first hit on trk,tpc,svt:
Distribution of first fitted space point with respect to z for TPC-only
global tracks. Should be approx. symmetric and flat around z=0. A peak
or hole at z=0 may indicate TPC calibration errors in either the t0
offset or the drift speed. Cross reference for calibration errors with z-DCA
vs tan1 (7.5).
3. StEHT globtrk: first point: hit - helix,tpc:
Residuals at FIRST point on track for TPC-only global tracks. The
quantities plotted are the longitudinal (along z-axis, dashed line) and
transverse (in x-y plane, solid line) differences between the
coordinates of the first hit and the DCA point on the helix fit to the
first point. For the transverse residual, positive (negative) values
correspond to hits inside (outside) the circular projection of the helix
onto the bend plane. FWHM should be less than ~ 1cm.
4. StEHT globtrk: phi of first point on trk,tpc:
Distribution of first fitted space point with respect to azimuthal angle
(phi) for TPC-only global tracks. The solid (dashed) line is for the
east (west) half of the TPC. These should be approximately equal and
flat within statistics, except for the 12-sector structure.
5. StEHT globtrk: chisq0,tpc:
Chi-square per degree of freedom for TPC global tracks.
Should peak just below 1.
6. StEHT globtrk: chisq1,tpc:
Probability of chi-square distribution for TPC global tracks.
Should peak at 1.
Page 11
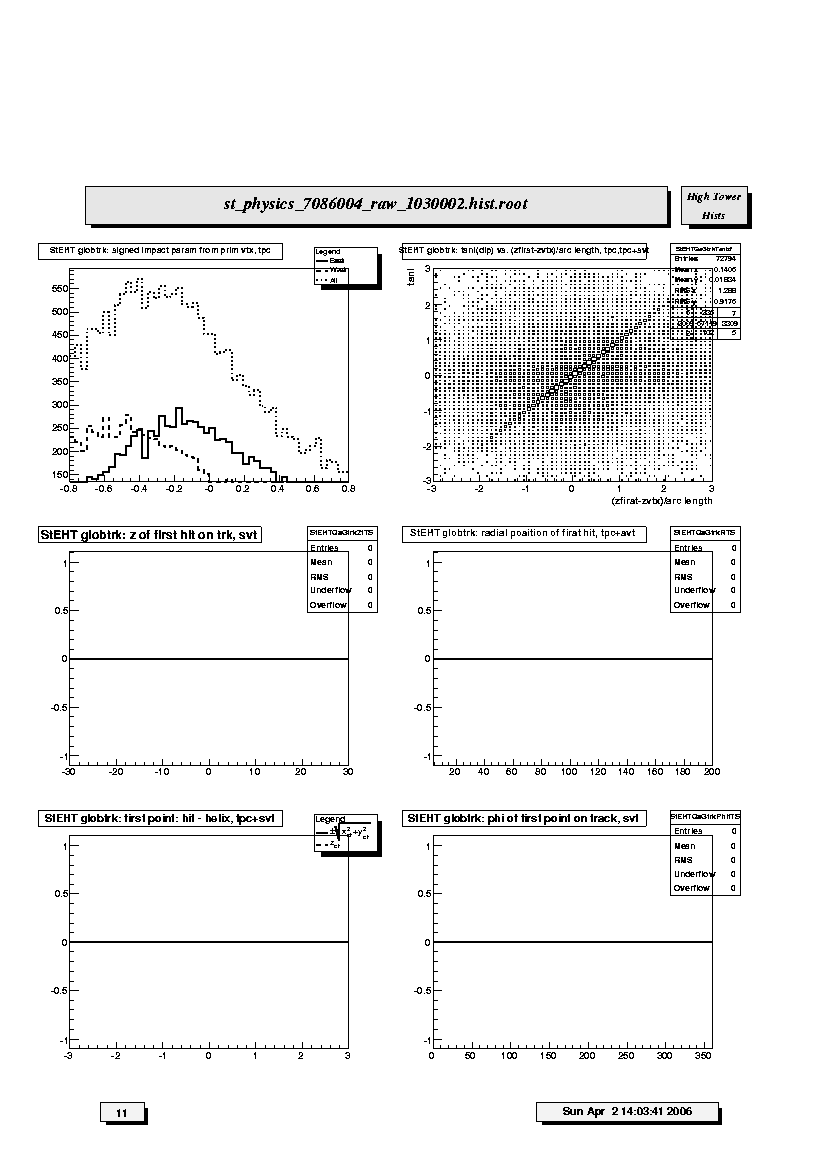
1. StEHT globtrk: signed impact param from prim vtx, tpc:
Two-dimensional (2D) (in the transverse plane) signed impact parameter
(in cm) from primary vertex for East (solid line), West (dashed line)
and All (dotted line) TPC-only global tracks. Should be centered at
zero.
2. StE globtrk: tan1(dip) vs. (zfirst-zvtx)/arc length,tpc,tpc+svt:
Scatter plot of tangent of dip angle (tanl) versus (z_first -
z_primvrtx)/arc-length for TPC-only global tracks and SVT+TPC global
tracks whose first fitted point is in the TPC. Variable 'z_first' is the
z coordinate of the first fitted point in the TPC. Variable 'z_primvrtx'
is the z-coordinate of the primary vertex for the event. Variable
'arc-length' is 2R*arcsin(delta_r/2R) where R = track radius of
curvature and delta_r is the transverse distance between the primary
vertex and the first hit on track. Primary tracks lie along the 45 deg
diagonal. Secondary tracks and strays lie scattered to either side. The
diagonal band should appear clearly and be straight and smooth without
kinks, breaks or bends.
3. StEHT globtrk: z of first hit on trk, svt:
Distribution of first fit hits with respect to z for SVT+TPC global
tracks which have the first fitted hit in the SVT. Should be flat within
statistics but could display steps at the ends due to the SVT layers.
Should be approximately symmetric but depends on distribution of primary
vertices.
4. StEHT globtrk: radial position of first hit, tpc+svt:
Distribution of radial position of first fitted hits on SVT+TPC global
tracks. Tracks on the right side correspond to those in which the SVT
space points were discarded by the fitter.
5. StEHT globtrk: first point: hit - helix, tpc+svt:
Residuals at FIRST point on track for SVT+TPC global tracks. The
quantities plotted are the longitudinal (along z-axis, dashed line) and
transverse (in x-y plane, solid line) differences between the
coordinates of the first hit and the DCA point on the helix fit to the
first point. For the transverse residual, positive (negative) values
correspond to hits inside (outside) the circular projection of the helix
onto the bend plane. FWHM should be less than ~ 0.1 cm. Broad, ~1 cm
wide tails, could be due to tracks in which the SVT hits were discarded
by the fitter.
6. StEHT globtrk: phi of first point on track, svt:
Distribution of first fitted space point with respect to azimuthal angle
(phi) for SVT+TPC global tracks with first point in the SVT. These
should be approximately equal and flat within statistics.
Page 12
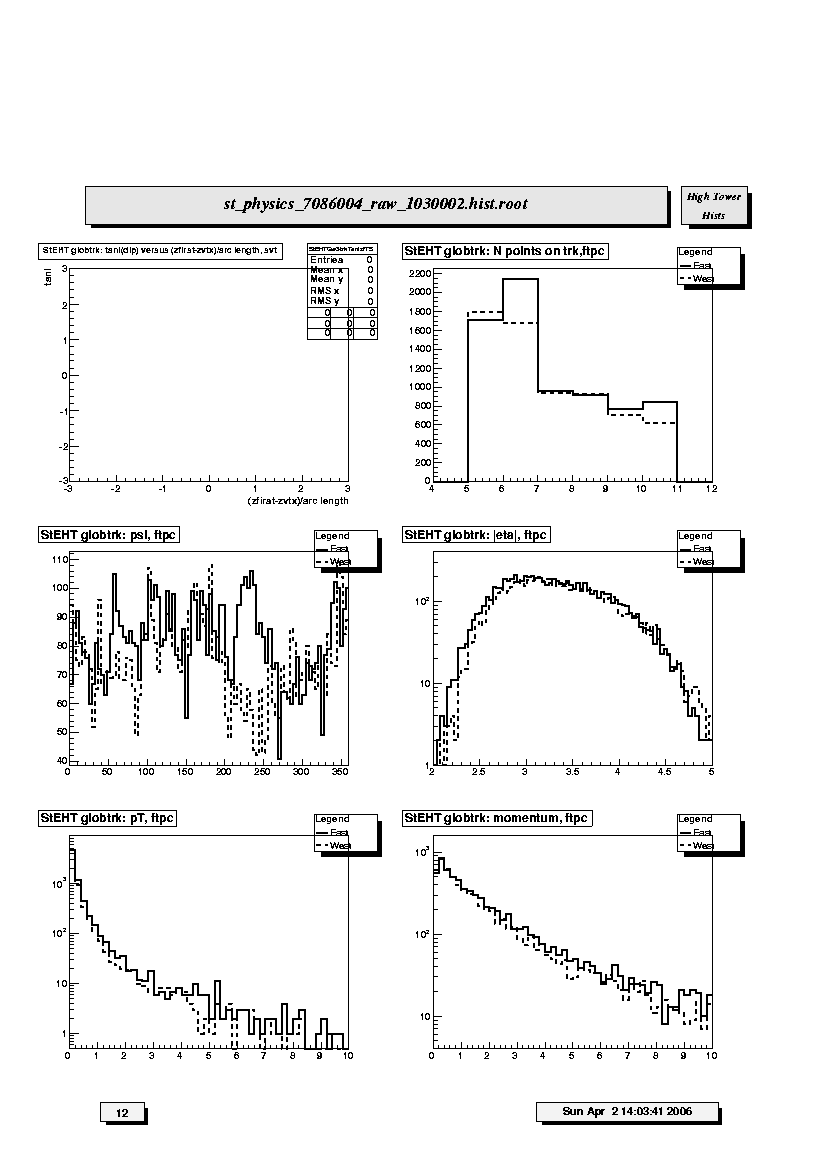
1. StEHT globtrk:tan1(dip) versus (zfirst-zvtx)/arc length,svt:
Scatter plot of tangent of dip angle (tanl) versus (z_first -
z_primvrtx)/arc-length for SVT+TPC global tracks with first point in the
SVT. Variable 'z_first' is the z coordinate of the first fitted point in
the SVT. Variable 'z_primvrtx' is the z-coordinate of the primary vertex
for the event. Variable 'arc-length' is 2R*arcsin(delta_r/2R) where R =
track radius of curvature and delta_r is the transverse distance between
the primary vertex and the first hit on track. Primary tracks lie along
the 45 deg diagonal. Secondary tracks and strays lie scattered to either
side. The diagonal band should appear clearly and be straight and smooth
without kinks, breaks or bends. This should be much cleaner than that
for the TPC-only tracks.
2. StEHT globtrk: N points on trk, ftpc:
Distribution of the number of fitted points on track for FTPC-East
(solid line) and FTPC-West (dashed line) global tracks. Distributions
should be similar within statistics, depending on the relative fraction
of active readout in each detector.
3. StEHT globtrk: psi, ftpc:
Azimuthal distributions for track direction angle (psi) for FTPC-East
(solid line) and FTPC-West (dashed line) global tracks. These should be
similar and flat within statistics except for the hexagonal FTPC sector
structure.
4. StEHT globtrk: |eta|,ftpc:
Distributions of absolute value of pseudorapidity for FTPC-East (solid
line) and FTPC-West (dashed line) global tracks. These should be similar
within statistics and range from about 2.5 to 4.5.
5. StEHT globtrk: pT,ftpc:
Transverse momentum (GeV/c) distributions for FTPC-East (solid line) and
FTPC-West (dashed line) global tracks. These should be similar within
statistics.
6. StEHT globtrk: momentum,ftpc:
Total momentum (GeV/c) distributions for FTPC-East (solid line) and
FTPC-West (dashed line) global tracks. These should be similar within
statistics.
Page 13
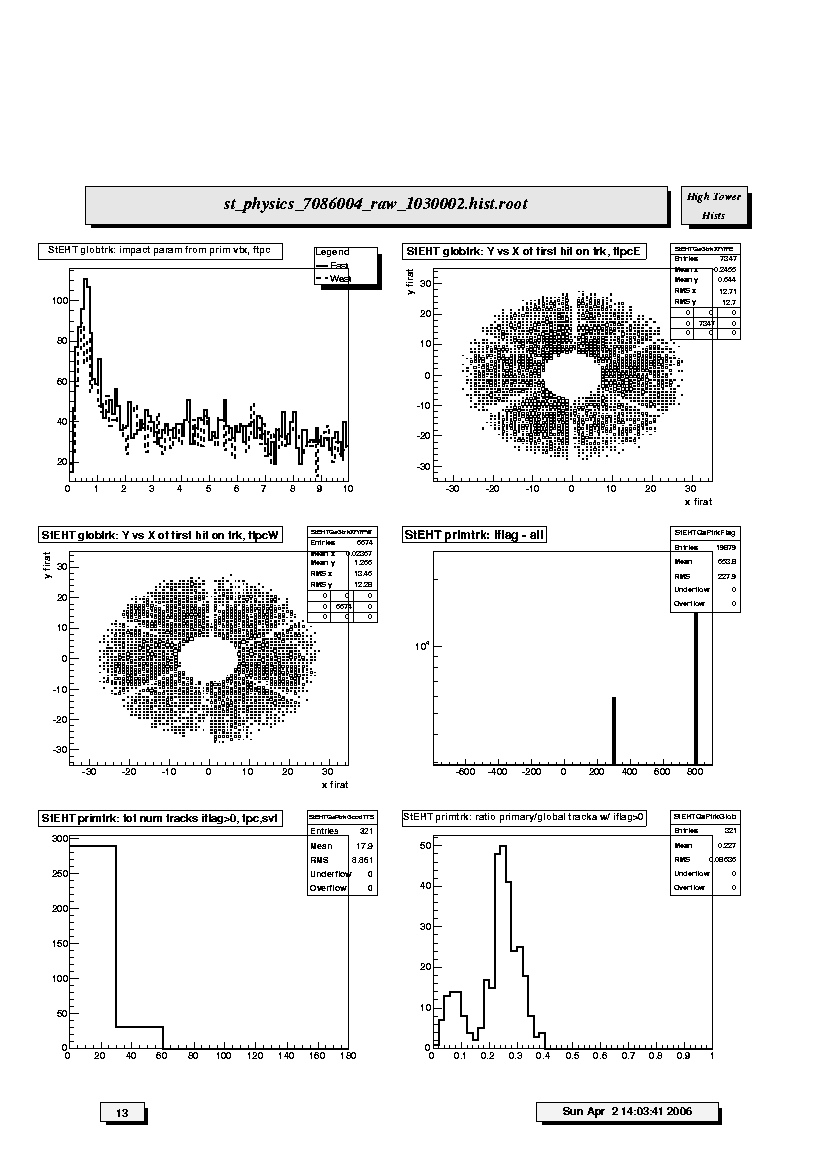
1. StEHT globtrk: impact param from prim vtx, ftpc:
Distribution of impact parameter values for global FTPC East tracks
(solid curve) and West tracks (dashed curve) with respect to the main
TPC global track determined primary vertex.
2. StEHT globtrk: Y vs X of first hit on trk, ftpcE:
Scatter plot of (x,y) coordinates for the first fitted space points in
FTPC-East global tracks. These should be uniformly populated with hits;
FTPC hexagonal structure is apparent.
3. StEHT globtrk: Y vs X of first hit on trk, ftpcW:
Scatter plot of (x,y) coordinates for the first fitted space points in
FTPC-West global tracks. These should be uniformly populated with hits;
FTPC hexagonal structure is apparent.
4. StEHT primtrk:iflag - all:
Quality flag values for all primary tracks. Some with large, negative
values may not appear on plot; check stat. box for underflows. Majority
of tracks should have iflag>0, corresponding to good, usable tracks.
Refer to: dst_track_flags.html and kalerr.html for description of flag
values.
5. StEHT primtrk: tot num tracks iflag>0, tpc, svt:
Good primary track multiplicity distribution for TPC-only and SVT+TPC
tracks. Magnitude and width depends on trigger condition and
multiplicity cut for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
6. StEHT primtrk: ratio primary/global tracks w/iflag>0:
Ratio of good primary to good global tracks for all detectors. Should be
of order 1/3 to 2/3.
Page 14
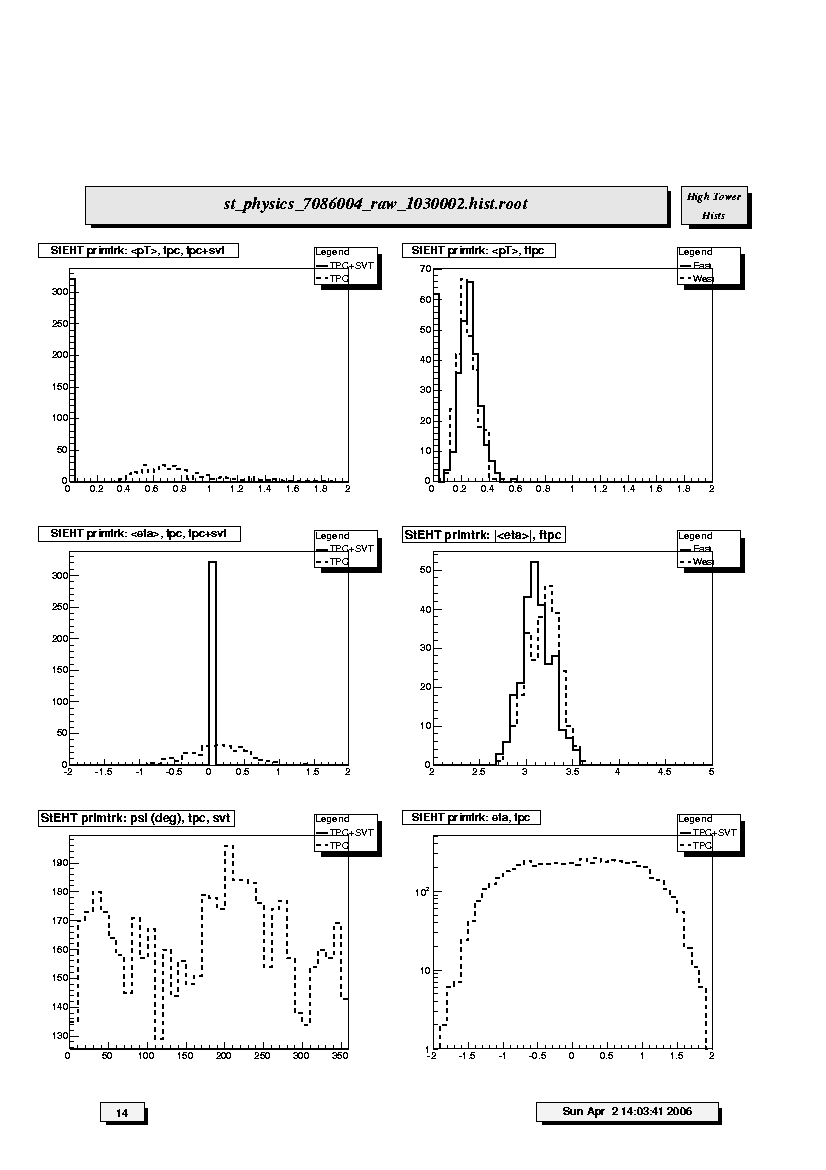
1. StEHT primtrk: <pT>,tpc,tpc+svt:
Mean transverse momentum distribution for TPC-only (dashed line) and
SVT+TPC (solid line) good primary tracks. Should peak around 0.4 - 0.6
GeV/c and be fairly narrow.
2. StEHT primtrk: <pT>,ftpc:
Mean transverse momentum distribution for FTPC-East (solid line) and
FTPC-West (dashed line) good primary tracks. These should be similar
within statistics and peak around 0.4 - 0.6 GeV/c but can have broader
distributions than for the SVT and TPC tracks.
3. StEHT primtrk: <eta>,tpc,tpc+svt:
Mean pseudorapidity distribution for TPC-only (dashed line) and SVT+TPC
(solid line) good primary tracks. Should peak around 0 but can be fairly
broad depending on distribution of primary vertices.
4. StEHT primtrk: |<eta>|,ftpc:
Distribution of absolute value of mean pseudorapidity for FTPC-East
(solid line) and FTPC-West (dashed line) good primary tracks. These
should be similar within statistics and peak around 3 - 3.5.
5. StEHT primtrk: psi(deg),tpc,svt:
Azimuthal distributions for track direction angle (psi) for TPC-only
(dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid line) good primary tracks. Should be
flat within statistics but may show the TPC sector gaps.
6. StEHT primtrk: eta,tpc:
Pseudorapidity (eta) distributions for TPC-only (dashed line) and
SVT+TPC (solid line) primary tracks. TPC tracks should be symmetric
about eta=0. SVT+TPC may have slight non-symmetry depending on
distribution of primary vertices.
Page 15
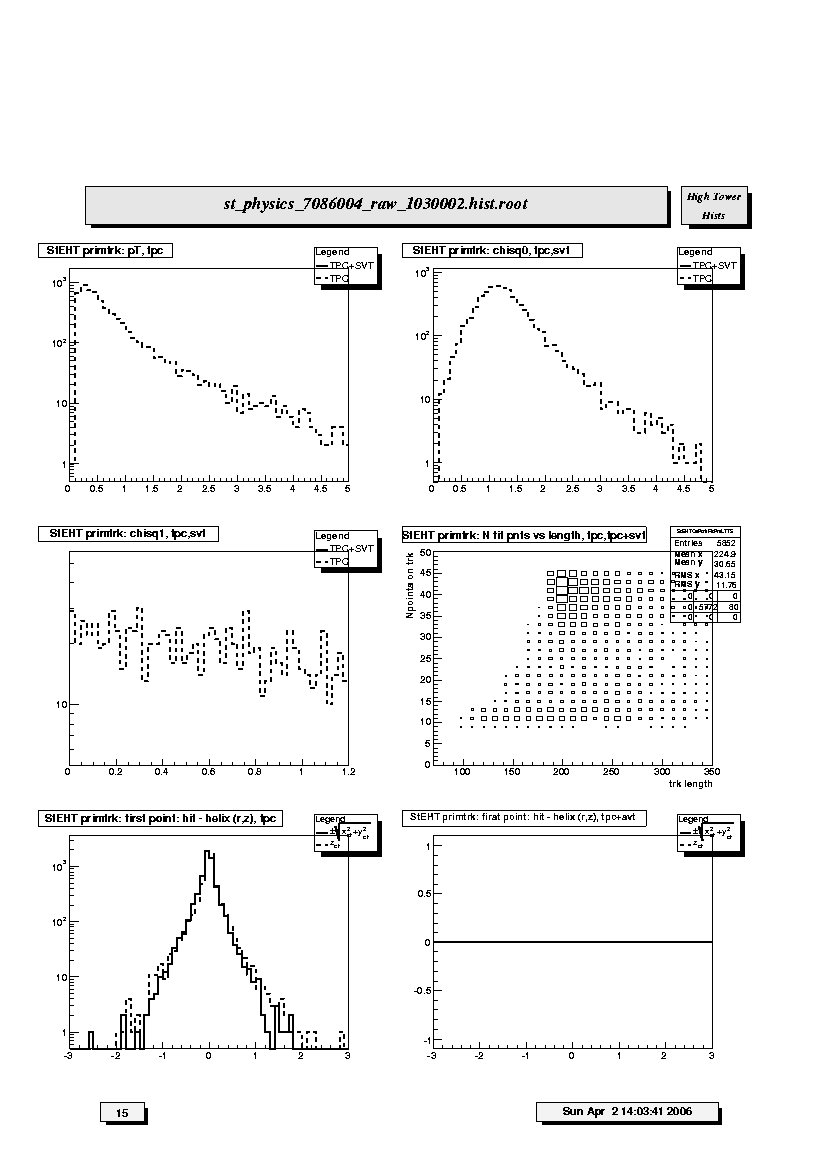
1. StEHT primtrk: pT,tpc:
Transverse momentum (GeV/c) distributions for TPC-only (dashed line) and
SVT+TPC (solid line) primary tracks.
2. StEHT primtrk: chisq0,tpc,svt:
Chi-square per degree of freedom for TPC-only (dashed line) and SVT+TPC
(solid line) primary tracks. Both should peak just below 1, but watch
for anomalously long tails at large chi-square.
3. StEHT primtrk: chisq1,tpc,svt:
Probability of chi-square for TPC-only (dashed line) and SVT+TPC (solid
line) primary tracks. Both should have strong peak at 1.
4. StEHT primtrk: N fit pnts vs length,tpc,tpc+svt:
Scatter plot of number of fitted points on track versus track length
(from first to last point along helical path) for both TPC-only and
SVT+TPC primary tracks. There should not be a peak in lower left corner
indicating fewer split tracks than for global tracks. There should be a
peak(s) for long tracks above 1.5 m.
5. StEHT primtrk: first point: hit - helix(r,z),tpc:
Residuals at first point on track for TPC-only primary tracks. The
quantities plotted are the longitudinal (along z-axis, dashed line) and
transverse (in x-y plane, solid line) differences between the
coordinates of the first hit and the DCA point on the helix fit to the
first point. For the transverse residual, positive (negative) values
correspond to hits inside (outside) the circular projection of the helix
onto the bend plane. FWHM should be less than ~ 1cm.
6. StEHT primtrk: first point: hit - helix(r,z),tpc+svt:
Residuals at first point on track for SVT+TPC primary tracks. The
quantities plotted are the longitudinal (along z-axis, dashed line) and
transverse (in x-y plane, solid line) differences between the
coordinates of the first hit and the DCA point on the helix fit to the
first point. For the transverse residual, positive (negative) values
correspond to hits inside (outside) the circular projection of the helix
onto the bend plane. FWHM should be less than ~ 0.1 cm. Broad, ~1 cm
wide tails could be due to tracks in which the SVT hits were discarded
by the fitter.
Page 16
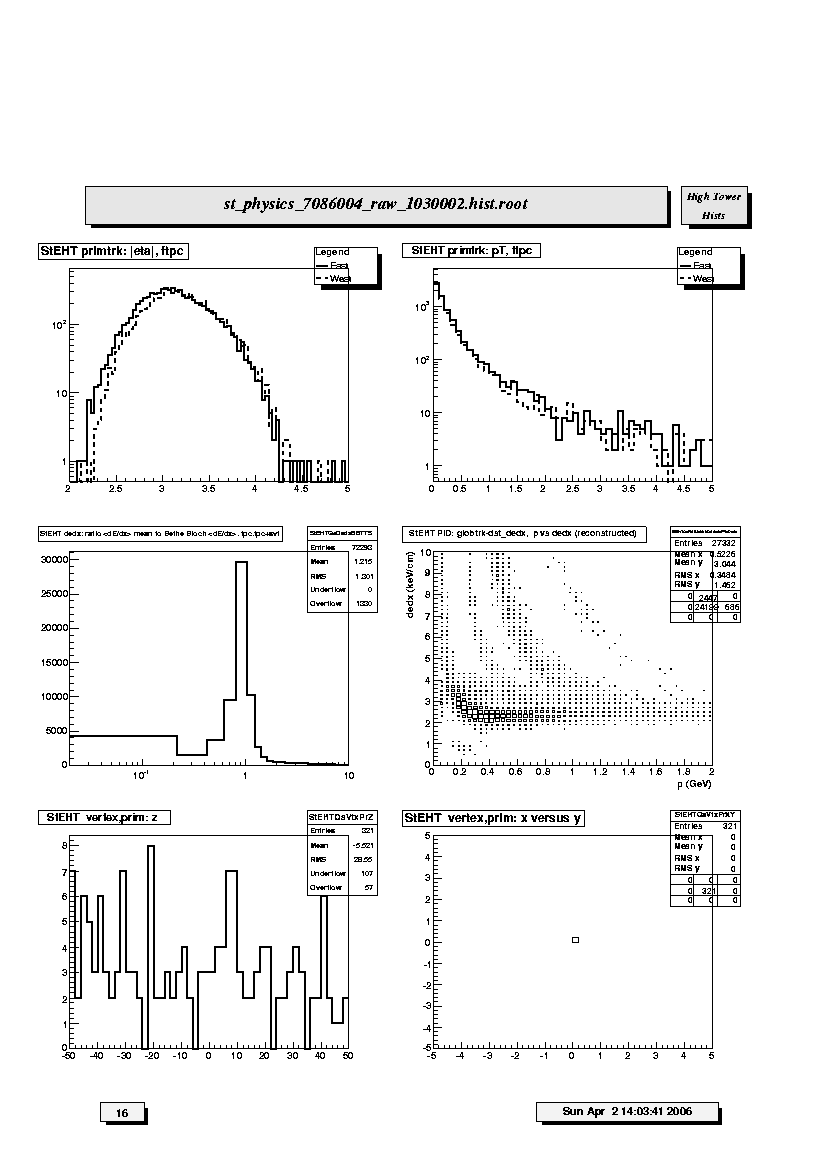
1. StEHT primtrk: |eta|,ftpc:
Distributions of absolute value of pseudorapidity for FTPC-East (solid
line) and FTPC-West (dashed line) primary tracks. These should be
similar within statistics and range from about 2.5 to 4.5.
2. StEHT primtrk: pT,ftpc:
Transverse momentum (GeV/c) distributions for FTPC-East (solid line) and
FTPC-West (dashed line) primary tracks. These should be similar within
statistics.
3. StEHT dE/dx: ratio <dE/dx> to Bethe-Bloch dE/dx,tpc,tpc+svt:
Distribution of ratio of mean dE/dx to Bethe-Bloch dE/dx for pions at
the same momentum for TPC-only and SVT+TPC global tracks. Should peak at
~1. Tests calibration of charge deposition in TPC gas.
4. StEHT PID: globtrk-dst_dedx, p vs dE/dx (reconstructed):
Scatter plot of truncated mean dE/dx versus total momentum (GeV/c) for
TPC-only and SVT+TPC global tracks. Should be able to see Bethe-Bloch
bands for pions, kaons and protons if statistics are sufficient.
5. StEHT vertex,prim: z:
Distribution of primary vertex position along the z-axis out to abs(z) <
50 cm.
6. StEHT vertex,prim: x versus y:
Scatter plot of the (x,y) coordinates of the primary vertex position.
This should correspond to the determined beam transverse position. The
amount of dispersion will depend on the trigger condition and
multiplicity cut for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
For p-p collisions the primary vertex transverse position is not determined;
all points are set to (0,0).
Page 17
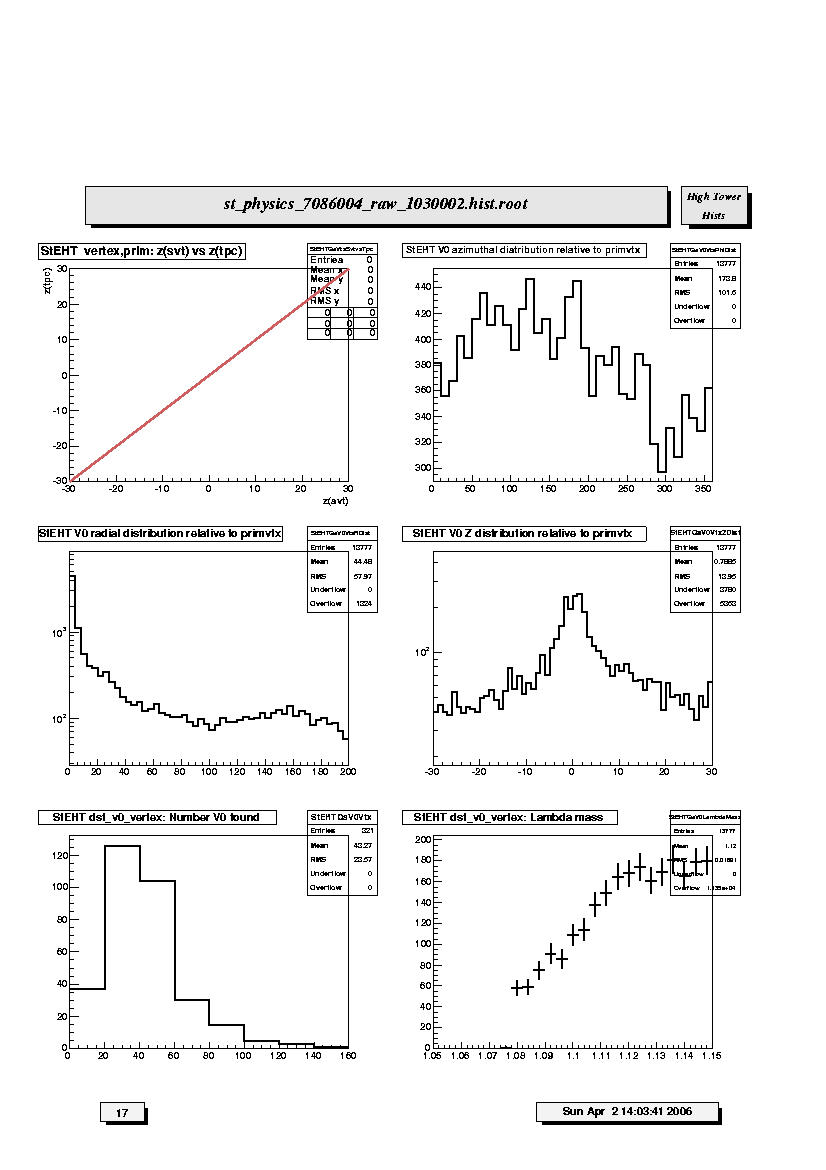
1. StEHT vertex,prim:z(svt) vs z(tpc):
Scatter plot of z-coordinate (beam line) position of primary vertices
determined by the SVT versus that determined by TPC global tracks
over the range |z| < 30 cm covered by the SVT. Points should lie
along the diagonal reference line.
2. StEHT V0 azimuthal distribution relative to prim vtx:
Azimuthal distribution of V0 vertices relative to the primary vertex for
each event. Should be flat within statistics.
3. StEHT V0 radial distribution relative to prim vtx:
Radial distribution of V0 vertices relative to the primary vertex for
each event. Should fall off steeply with most vertices within ~10 cm.
4. StEHT V0 z distribution relative to prim vtx:
Longitudinal (z) distribution of V0 vertices relative to the primary
vertex for each event. Should fall off steeply with most vertices within
~10 cm.
5. StEHT dst_v0_vertex: Number V0 found:
Total number of V0 vertices found in each event; should scale with
multiplicity. Range depends on trigger condition and multiplicity cut
for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
6. StEHT dst_v0_vertex: Lambda mass:
Invariant mass plot of V0 vertices using Lambda decay hypothesis.
Sometimes possible to see Lambda peak for low- and mid-multiplicity events.
Page 18
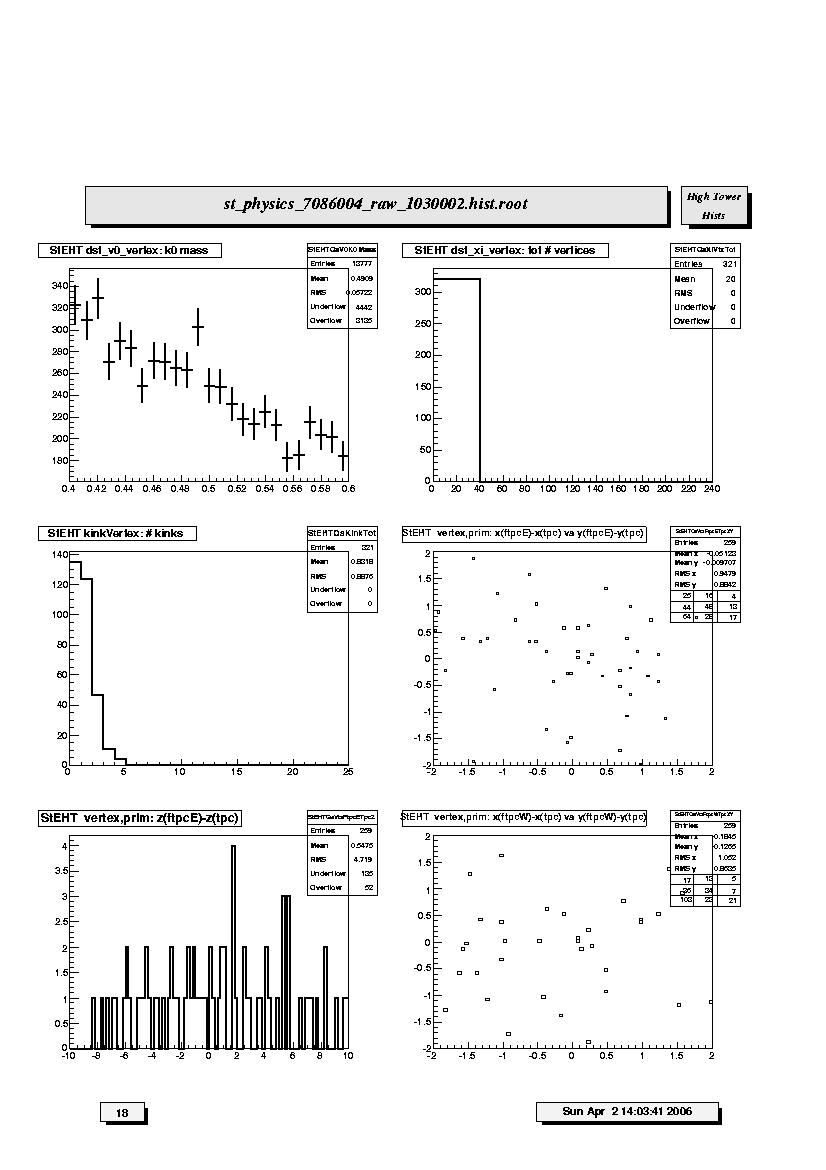
1. StEHT dst_v0_vertex: k0 mass:
Invariant mass plot of V0 vertices using K0-short decay hypothesis.
Sometimes possible to see K0-short peak for low- and mid-multiplicity
events.
2. StEHT dst_xi_vertex: tot # vertices:
Total number of Xi vertex candidates found in each event; should scale
with multiplicity. Range depends on trigger condition and multiplicity
cut for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium or high).
3. StEHT kinkVertex: # kinks:
Total number of kink decay vertex candidates found in the TPC for
each event; should scale with multiplicity. Range depends on trigger
condition and multiplicity cut for this set of plots (i.e. low, medium
or high).
4. StEHT vertex,prim:x(ftpcE)-x(tpc) vs y(ftpcE)-y(tpc):
Scatter plot of the differences in x-y position (cm) for primary vertex
positions determined by FTPC East global tracks and main TPC glbtrks.
Should scatter about (0,0).
For p-p collisions the primary vertex x-y positions are not determined;
the scatter reflects the FTPC East vertex determination.
5. StEHT vertex,prim:z(ftpcE)-z(tpc):
Distribution of the differences along the z-axis, i.e. beam direction,
in cm for primary vertex positions determined by FTPC East global
tracks and main TPC glbtrks. The mean should be near 0.
6. StEHT vertex,prim:x(ftpcW)-x(tpc) vs y(ftpcW)-y(tpc):
Scatter plot of the differences in x-y position (cm) for primary vertex
positions determined by FTPC West global tracks and main TPC glbtrks.
Should scatter about (0,0).
For p-p collisions the primary vertex x-y positions are not determined;
the scatter reflects the FTPC West vertex determination.
Page 19
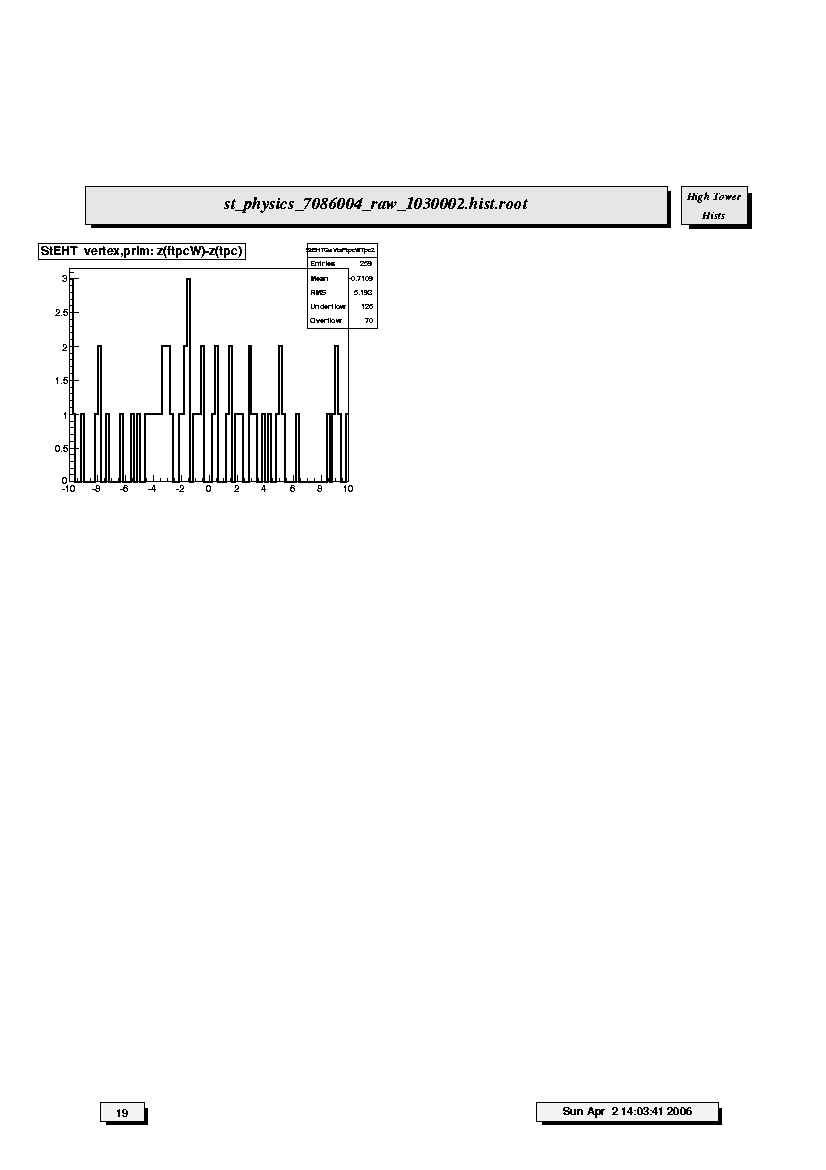
1. StEHT vertex,prim:z(ftpcW)-z(tpc):
Distribution of the differences along the z-axis, i.e. beam direction,
in cm for primary vertex positions determined by FTPC West global
tracks and main TPC glbtrks. The mean should be near 0.


















