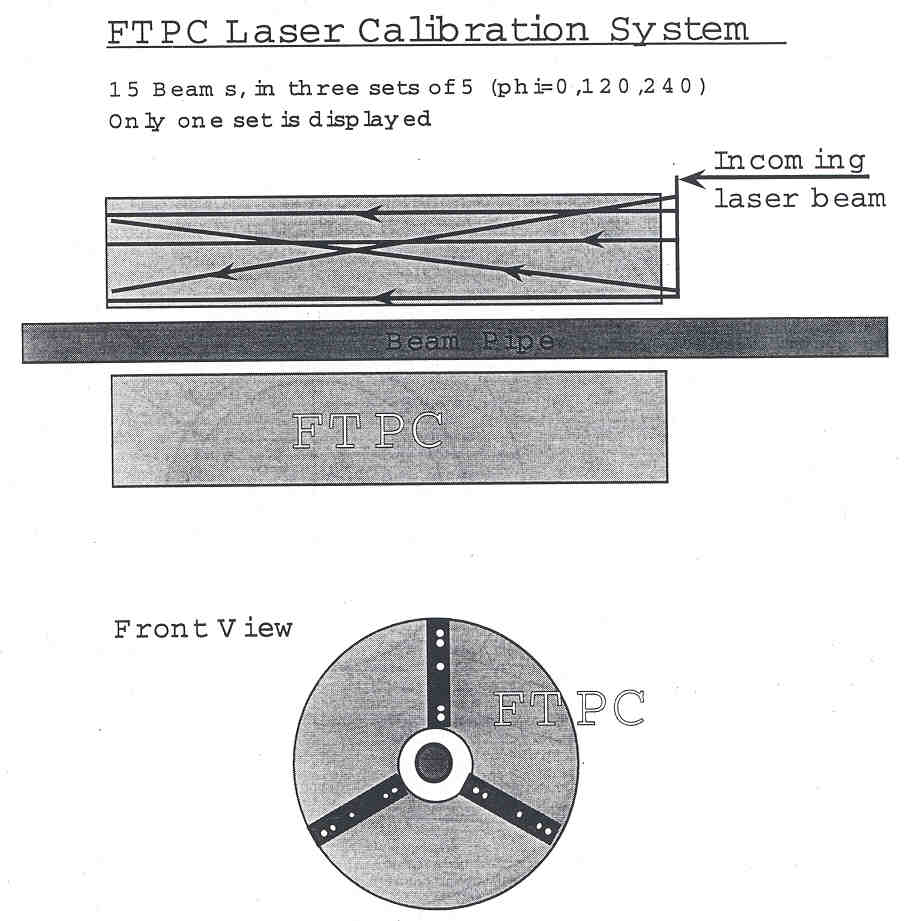

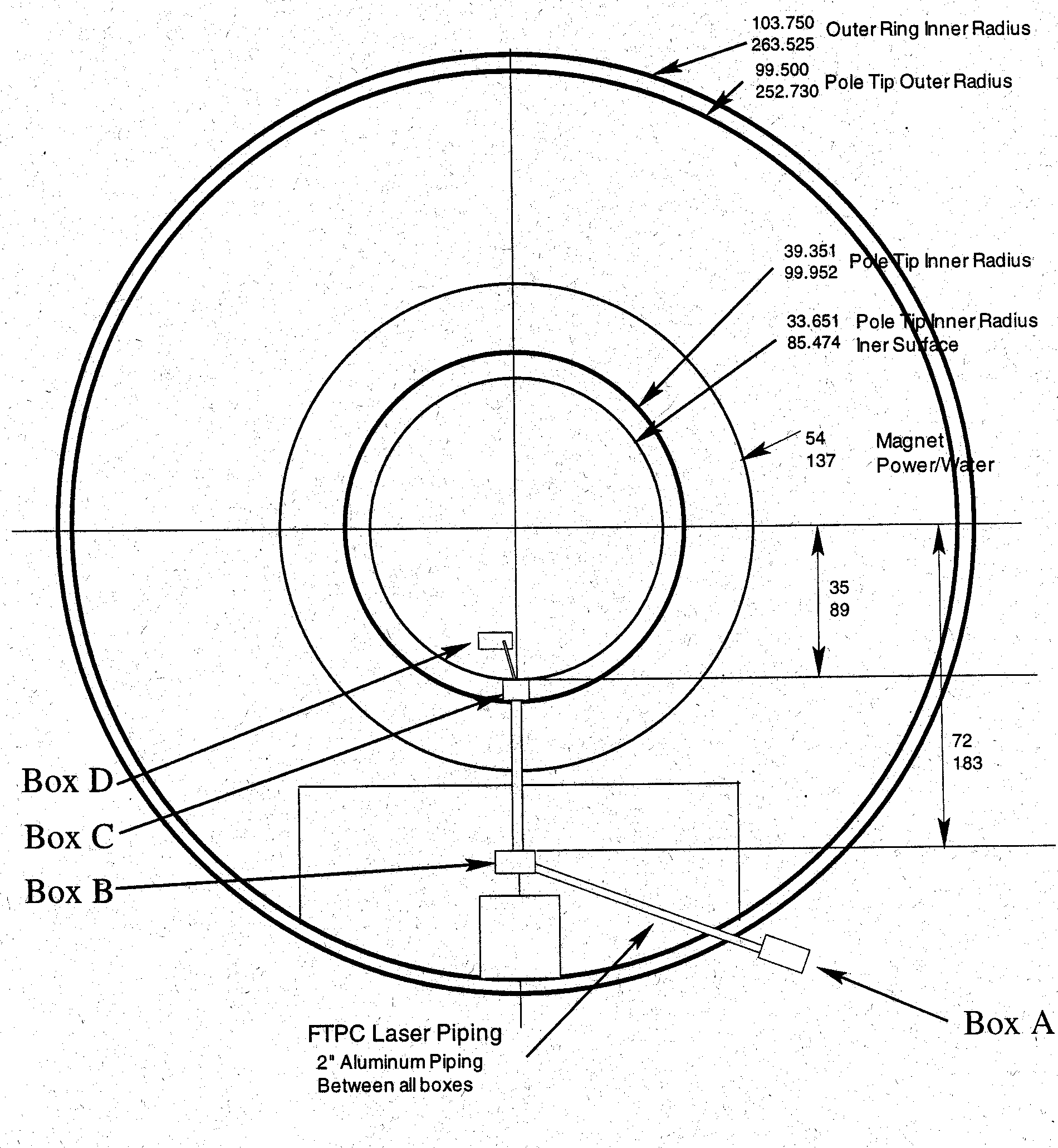
The path of the laser beam from the flipper mirror (in the box labelled
as Box A) through two mirror boxes on the magnet poletip (Boxes B and C)
to the distribution box (Box D) on the face of the FTPC. This part
of the system is being developed at BNL by Alexei
Lebedev.
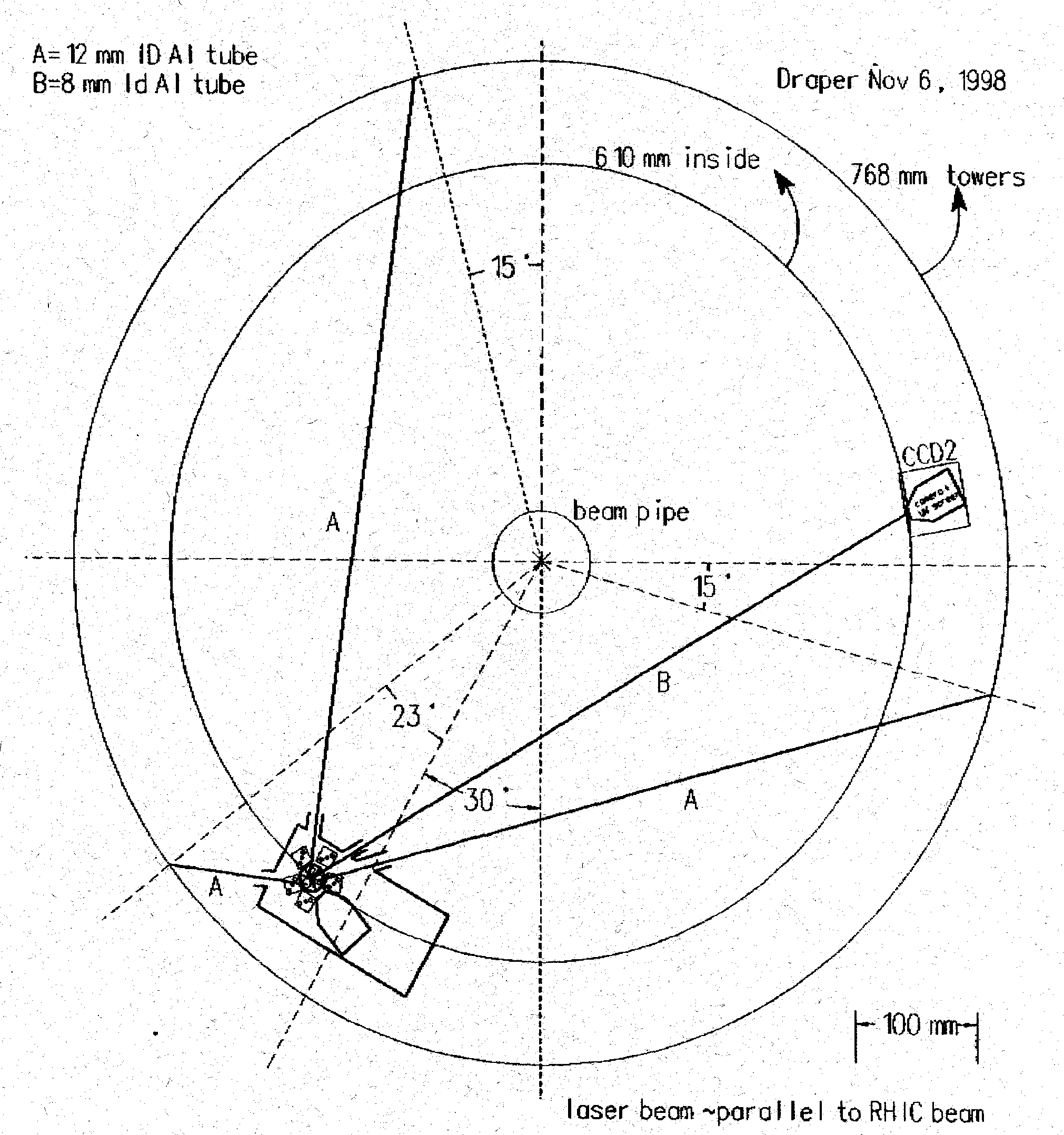
Schematic drawing of the distribution of the laser beams from Box D
to the three insertion rods and a monitoring camera (CCD2) on the face
of the FTPC. The components indicated inside Box D are not equivalent to
the current design.
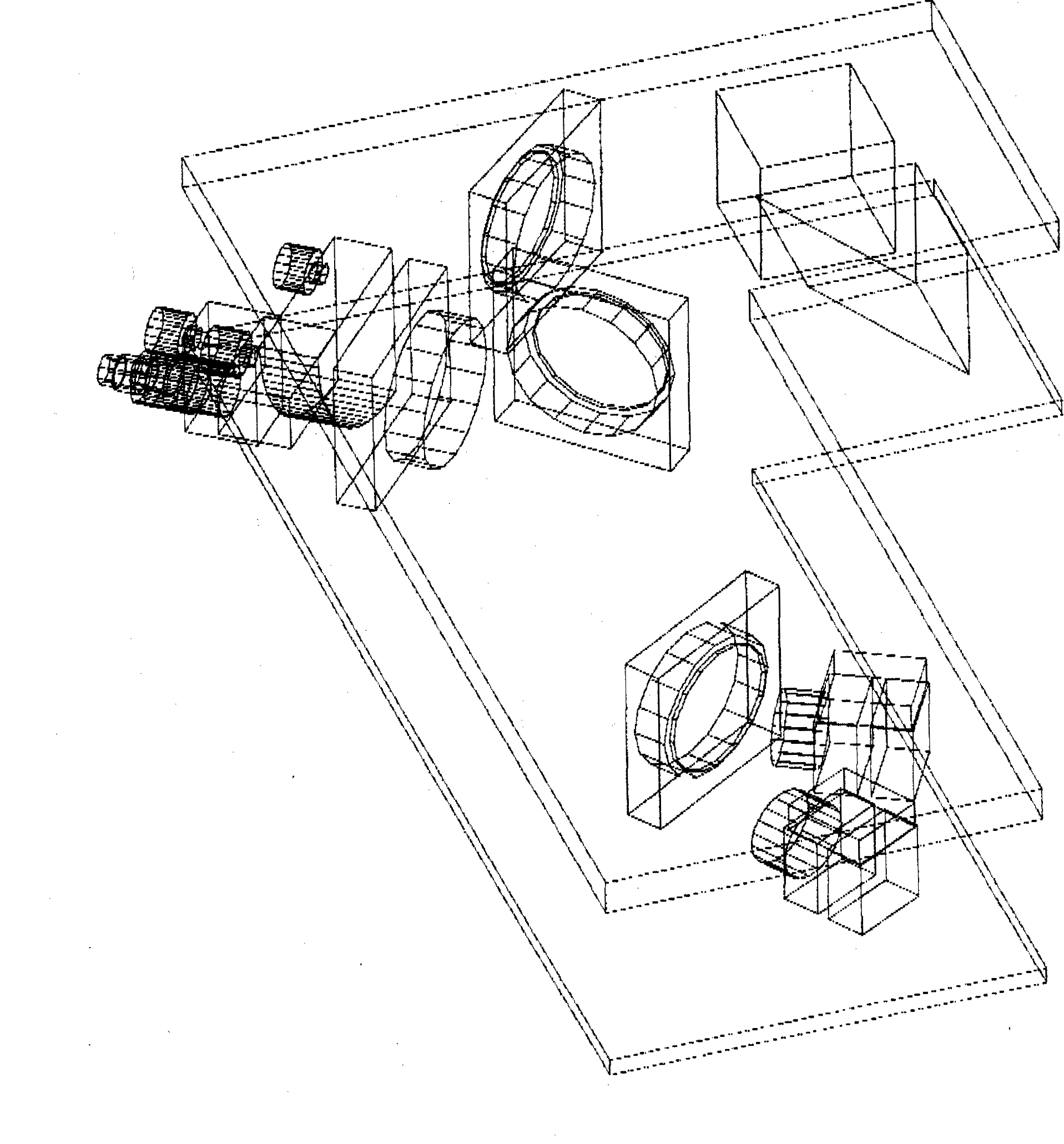
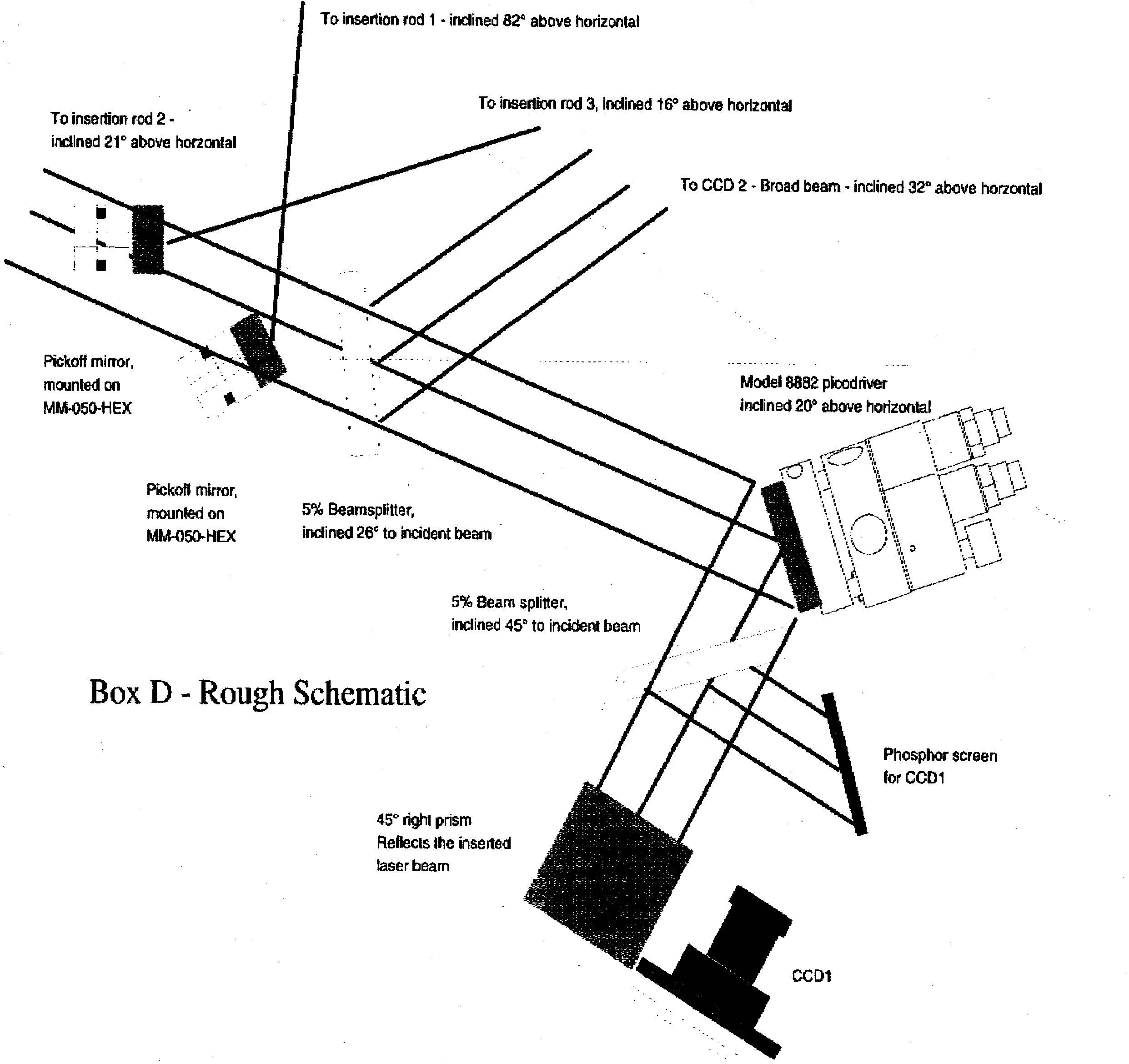
Schematic drawing of the components inside Box D. 5% of the intensity
are reflected out of the beam for observation by a CCD camera (CCD 1),
which supervises the location of the beam upon arrival at Box D.
A mirror with a remote controlled picodriver provides a last possibility
to adjust the direction of the beam, supervised by CCD 2. Two small pickoff
mirrors then reflect parts of the beam to two insertion rods, the remaining
part continues on to the third insertion rod. Box D is designed at BNL
by Daniel Cebra and Alexei
Lebedev.
3d-view of the Box D design: