Next: Summary Up: Cross Section Previous: Cross Section Contents
The following sources of systematic errors are considered in the analysis:
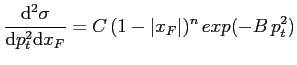 |
(6.21) |
To obtain the total systematic error, the errors are combined in the following way
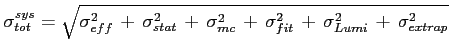 |
(6.22) |
The presented analysis is clearly dominated by systematic errors.
A systematic error due to the deviations in the ![]() and
and ![]() can be
reduced by improving the kinematical model used for
can be
reduced by improving the kinematical model used for ![]() generation, for example by
introducing two slopes into the
generation, for example by
introducing two slopes into the ![]() distribution, as was mentioned above.
A further improvement of the detector description in simulated events is needed.
All sources of the systematic errors are listed in the Table 6.12.
distribution, as was mentioned above.
A further improvement of the detector description in simulated events is needed.
All sources of the systematic errors are listed in the Table 6.12.
|