



Next: Readout and Data Acquisition
Up: Means of particle identification
Previous: The Cherenkov counters
Contents
Kopytine's homepage
NA44 uses nine stacks of a fine-sampling Uranium/Copper/scintillator
Calorimeter with wavelength shifter readout, originally designed [32]
for the AFS experiment at ISR.
Each stack is sub-divided into six towers.
Each tower has two sections, read out separately: a 6 radiation lengths
(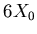 )
long electromagnetic one, and a 3.8 absorption lengths
(
)
long electromagnetic one, and a 3.8 absorption lengths
(
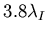 ) long hadronic absorber.
Each section is read out by two PMTs collecting light from two light guides that
cover left and right flanks of the section.
) long hadronic absorber.
Each section is read out by two PMTs collecting light from two light guides that
cover left and right flanks of the section.
![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.gif) Two characteristic features of this device are
Two characteristic features of this device are
- nearly identical response to charged and neutral pions
![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/footnote.gif) (not required by NA44)
(not required by NA44)
- self-calibration by measuring fission signal.
NA44 uses UCAL for 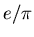 separation.
In particular, in this analysis UCAL was used to determine how many pions are
lost due to the Cherenkov electron veto in the trigger
(see subsection 4.4.3).
This is possible due to the longitudinal separation of the tower into
electromagnetic and hadronic sections.
The electromagnetic showers tend to have a predominant contribution from the
electromagnetic section.
Due to the low track multiplicity in the spectrometer, the UCAL's granularity
is sufficient to associate tracks with towers.
separation.
In particular, in this analysis UCAL was used to determine how many pions are
lost due to the Cherenkov electron veto in the trigger
(see subsection 4.4.3).
This is possible due to the longitudinal separation of the tower into
electromagnetic and hadronic sections.
The electromagnetic showers tend to have a predominant contribution from the
electromagnetic section.
Due to the low track multiplicity in the spectrometer, the UCAL's granularity
is sufficient to associate tracks with towers.




Next: Readout and Data Acquisition
Up: Means of particle identification
Previous: The Cherenkov counters
Contents
Mikhail Kopytine
2001-08-09