|
star focus:
Long range rapidity correlations
Highlights from the STAR papers:
Long range rapidity correlations and jet production in high energy nuclear collisions
and
Growth of Long Range Forward-Backward Multiplicity
Correlations with Centrality in Au+Au Collisions at
sqrt(sNN) = 200 GeV
.
Submitted for publication to Physical Review C and Physical
Review Letters respectively.
|
|
The STAR experiment has now reported two interesting
results on long range correlations
in rapidity. One of the experimental observation
is from a correlation study in azimthal angle and
pseudorapidity for produced charged hadrons with
respect to a particle with larger transverse momentum. Such
studies revealed a jet-like
correlation at small pair phase space separation
(in azimuth and pseudorapidity - near side) which
seems to be unmodified in central Au+Au
collisions relative to d+Au and a significant
correlated yield in central Au+Au collisions at
large pair separation in pseudorapidity (the
RIDGE). The ridge is observed in Au+Au collisions
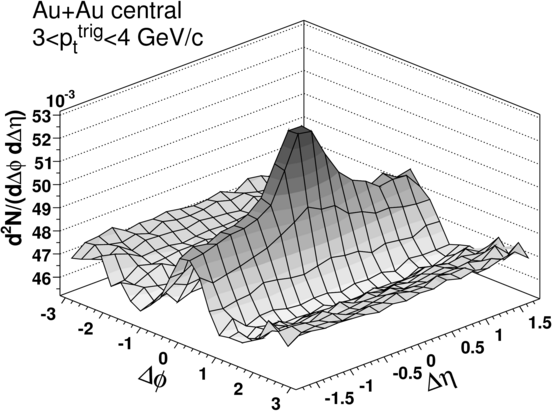
and not observed in d+Au collisions (See figures).
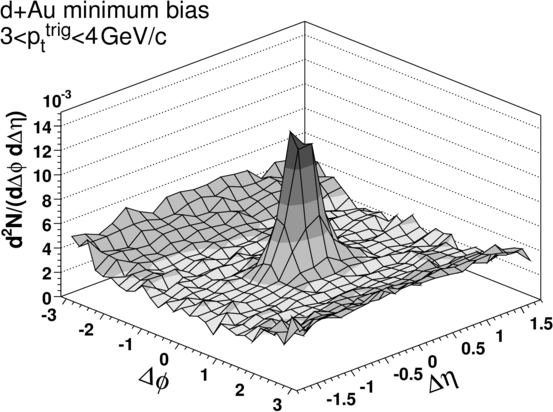
Several models have been proposed to explain the
observed broadening of the near-side distributions and the
occurrence of the ridge
since we first reported this at RHIC. Models
based on radiative partonic energy loss suggest
that the ridge arises from the coupling of
induced gluon radiation to the longitudinal flow of bulk
matter, or from the coupling of radiation
to transverse chromo-magnetic fields. Other
models attribute the ridge to the effect of
elastic scattering of the jet in the flowing
medium,
to medium heating by a jet,to radial
flow of bulk matter in coincidence with a jet
trigger bias due to energy loss,or to long-range
rapidity correlations arising from a Color Glass
Condensate initial state. For knowing further
details of the properties of the ridge please
read the STAR paper [1].
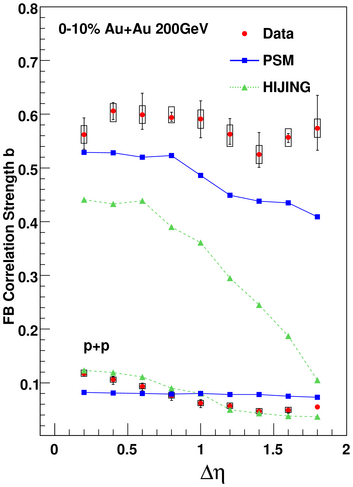
We also obtain the long range correlations strength (b) by
measuring the magnitude of the
forward-backward multiplicity correlation over a
long range in pseudorapidity. The correlation
strength is found (see figure) to be almost constant as a
function of gap in pseudorapidity.
A decrease in such correlations as a function of
gap in pseudorapidity would have indicated presence of
strong short range correlations.
The magnitude of the correlations in central
Au+Au is much larger compared to p+p collisions.
Models like the Dual Parton Model and Color Glass
Condensate argue that the such long range
correlations are produced by multiple parton-
parton interactions. For further details of the
results take a look at STAR paper
[2].
Further details can be found in the following STAR papers -
Long range rapidity correlations and jet production in high energy nuclear collisions
- arXiv:0909.0191
and
Growth of Long Range Forward-Backward Multiplicity Correlations with Centrality in Au+Au Collisions at sqrt(sNN) = 200 GeV
- arXiv:0905.0237.
Previous STAR Focus Features
Posted: Sep 5, 2009
| 
