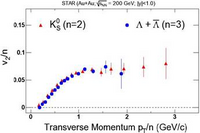
Figure. The measured azimuthal anisotropy parameter
divided by the number of quark constituents in the hadron as a function of
transverse momentum divided by the number of quark constituents for
K0s, and Lambda+anti-Lambda for Au-Au collisions at
200 GeV. The error bars are statistical only.
|
Apparent scaling for the azimuthal anisotropy of Lambda and K0s
In Au-Au collisions at RHIC one of the first measurements was the
observation of collective harmonic flow for charged hadrons and that this
flow showed a strong pt dependence. This observation has since
been extended to that the identified particles. The
K0s and Lambda+anti-Lambda also show a strong
pt dependence in the measured v2. However, they also
show that the value of v2 at a given pt is mass
dependent. This mass dependence is predicted hydrodynamical models and the
magnitude is in agreement with the STAR measured results up to
pt ~2 GeV/c . Above this transverse momentum the measured
v2 seems to saturate, this is in contradiction with
hydrodynamic
predictions. For pt /n > 0.8 GeV/c, where n is the number of
constituent quarks in the hadron, it is interesting to note that the
measured v2/n of the K0s and
Lambda+anti-Lambda is equal. If hadrons at intermediate pt are
created via coalescence of co-moving quarks from bulk partonic matter it
is
predicted that the v2 /n of the measured particles would behave
in such a fashion. In such a scenario this measurement reveals that the
partons develop an momentum-space azimuthal anisotropy created by the
ellipsoidal shape of the initial collision.
Related STAR papers
Particle-type dependence of azimuthal anisotropy and nuclear modification of particle production in Au+Au collisions at sqrt(snn) = 200 GeV
Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 (2004) 052302
e-Print Archives (nucl-ex/0306007):
Abstract |
PS |
PDF
Journal article:
Phys. Rev. Lett. server
Azimuthal anisotropy of K0s and Lambda + Lambdabar production at mid-rapidity from Au+Au collisions at sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV
Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 (2002) 132301
e-Print Archives (hep-ex/0205072):
Abstract |
PS |
PDF
Journal article:
Phys. Rev. Lett. server
| 
