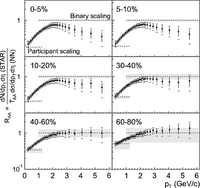
Figure. RAB as a function of pT for six centrality classes at
sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV.
|
Centrality dependence of high pT hadron suppression in Au+Au collisions at sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV
The first Au+Au collisions at RHIC were recorded in 2000 at center of
mass energy sqrt(snn) =
130 GeV. STAR measured the spectra of charged hadrons as a function of
transverse momentum and centrality.
These data were compared to a composite reference spectrum of p+p
collisions for the same beam energy in
order to evaluate nuclear effects on hadron production at high pT. The
ratio RAB =
(d2NAB/dpT deta) / (TAB
d2sigmapp/dpT deta)
where d2NAB/dpT deta is the differential yield per
event in the
nuclear collision A+B, TAB=< Nbinary>
sigmappinel describes
the nuclear geometry, and d2sigmapp/dpT deta is for
p+p inelastic collisions.
< Nbinary> is the mean number of binary NN interactions for
the given centrality class of
A+B collisions. In the absence of nuclear effects such as shadowing, the
Cronin effect, or
gluon saturation, hard process rates are expected to scale with <
Nbinary> and
RAB=1.
However, STAR observed that at the highest pT, hadron suppression of
approximately a factor 4-5 is observed
for the most central collisions: inclusive hadron production is strongly
suppressed at high pT in central Au+Au collisions. For the most peripheral
collisions RAB is
consistent with unity, while intermediate centralities interpolate smoothly
between the extremes.
These data are consistent with a scenario in which jets produced early
in the collision interact
strongly with the medium, reducing the yields of "leading" charged hadrons
compared to the yields from p+p
collisions, where no medium is present.
Related STAR papers
Centrality Dependence of High pT Hadron Suppression in Au + Au Collisions at sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV
Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 (2002) 202301
e-Print Archives (nucl-ex/0206011):
Abstract |
PS |
PDF
Journal article:
Phys. Rev. Lett. server
| 
