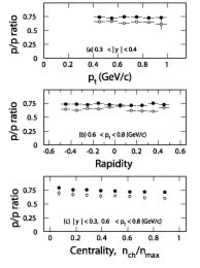
Figure. The pbar/p ratio from Au+Au collisions at sqrt(snn)
= 130 GeV (a) as a function of pT within the rapidity
range 0.3
< |y| < 0.4; (b) as a function of y within 0.6 <
pT
< 0.8 GeV/c; (c) as a function of collision centrality within
|y| < 0.3
and 0.6 < pT < 0.8 GeV/c from the reanalysis
(solid
circles) compared to the previous publication (open circles). Panels (a)
and (b)
show results for minimum bias collisions.
|
Midrapidity Antiproton-to-Proton Ratio from Au+Au Collisions at sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV
The primary goal of the heavy-ion collision program at the Relativistic
Heavy Ion
Collider (RHIC) is to create and study a novel state of matter constituted
of deconfined
quarks and gluons, named quark-gluon plasma. The formation of such a
deconfined state
depends on the initial conditions of the matter created at the early stage
of heavy-ion
collisions. One of the important observables is the baryon number transport
(or stopping)
that is achieved mostly at the early stage. The degree of baryon stopping
affects the
overall dynamical evolution of these collisions, and the measurement of the
antiproton-to-proton (pbar/p) yields may provide information on the
baryon transport.
The pbar/p ratio at midrapidity was measured by STAR in Au+Au
collisions at
sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV. The ratio is independent of tranverse
momentum
(pT) and rapidity (y) within |y| < 0.5 and
0.4
< pT < 1.0 GeV/c (see panels (a) and (b) in the
Figure). In
the same kinematic range, the average pbar/p ratio is 0.73 +-
0.003(stat) +- 0.05(syst)
for minimum bias collisions. In the centrality interval measured, no strong
centrality
dependence is observed (see panel (c) in the Figure). The measured
pbar/p ratio
indicates that even though the antibaryon-baryon (pbar-p) pair
production becomes
important at midrapidity, a significant excess of baryons over anti-baryons
is still
present in heavy-ion collisions at RHIC. The comparison of the STAR
measurement at
RHIC to heavy-ion results at lower energies (AGS and SPS) indicate that the
midrapidity
pbar/p ratio in heavy-ion collisions increases significantly with
collision energy.
Related STAR papers
Midrapidity Antiproton-to-Proton Ratio from Au+Au sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV
Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 (2001) 4778
e-Print Archives (nucl-ex/0104022):
Abstract |
PS |
PDF
Journal article:
Phys. Rev. Lett. server
Erratum: Midrapidity Antiproton-to-Proton Ratio from Au+Au sqrt(snn) = 130 GeV [Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 (2001) 4778]
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 (2003) 119903(E)
Journal article:
Phys. Rev. Lett. server
| 
